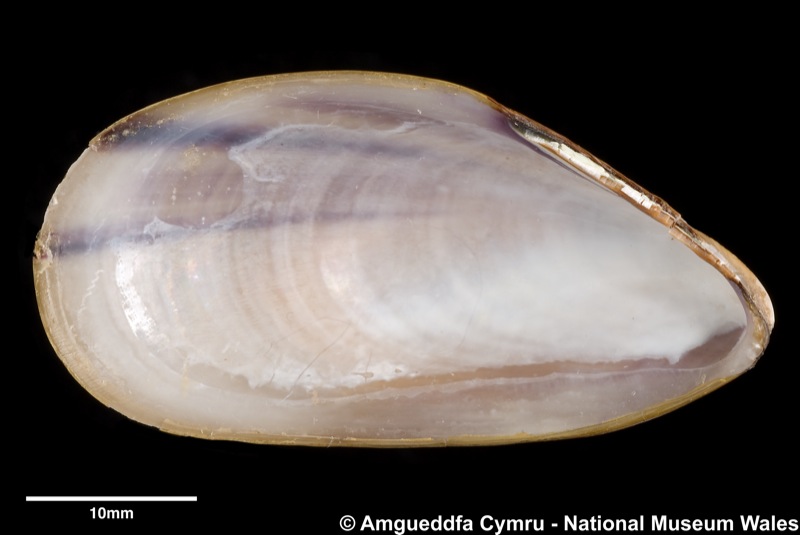
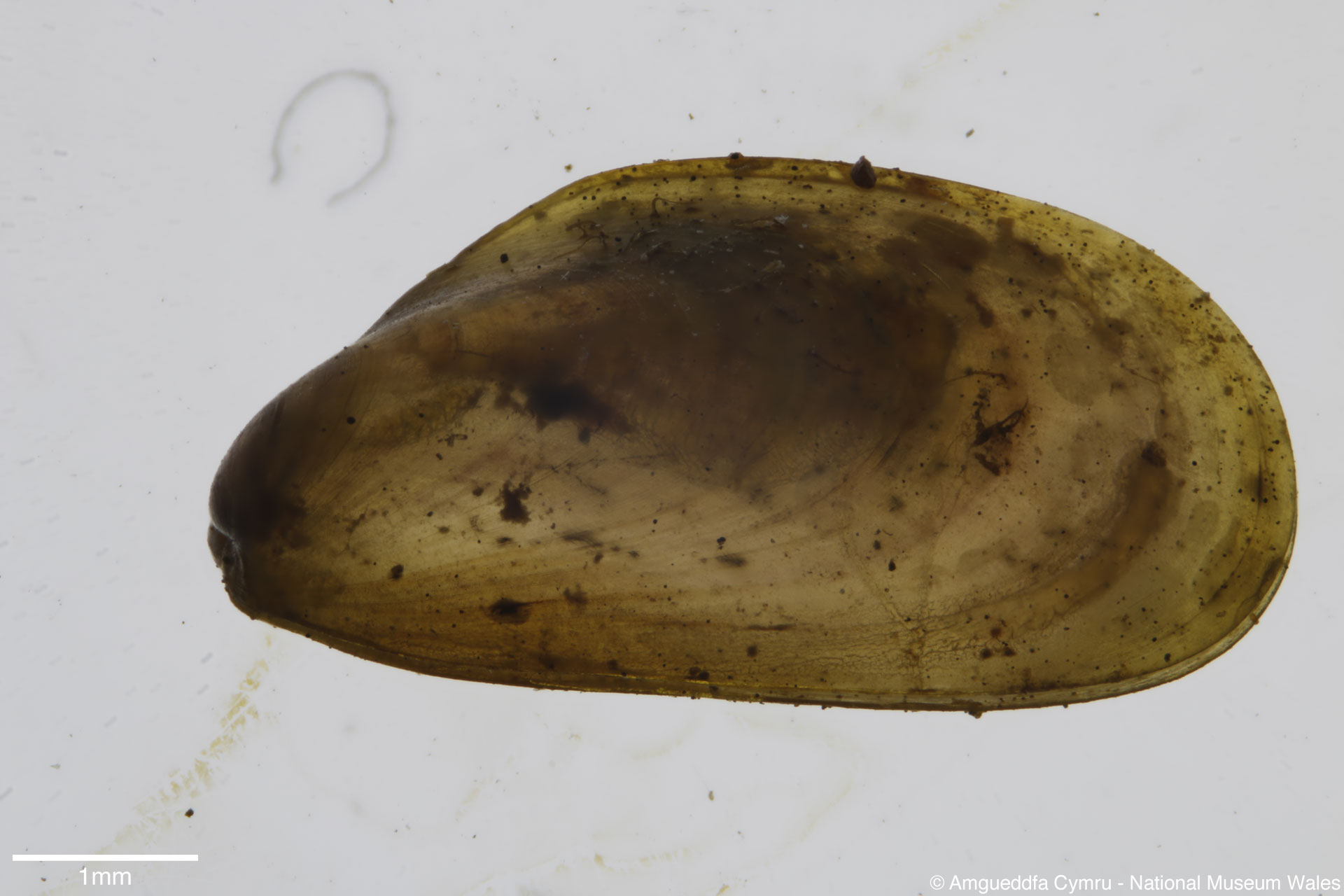
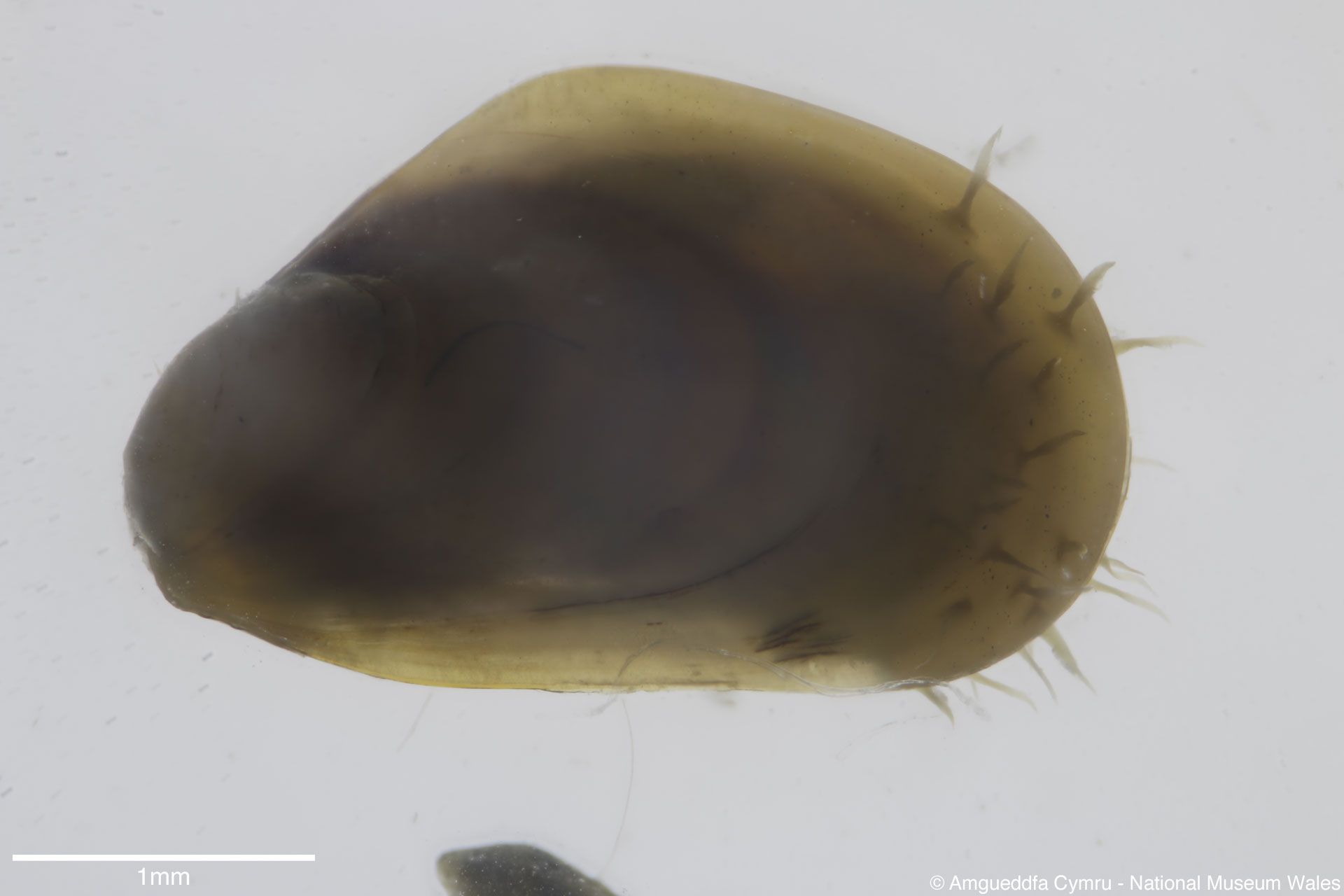
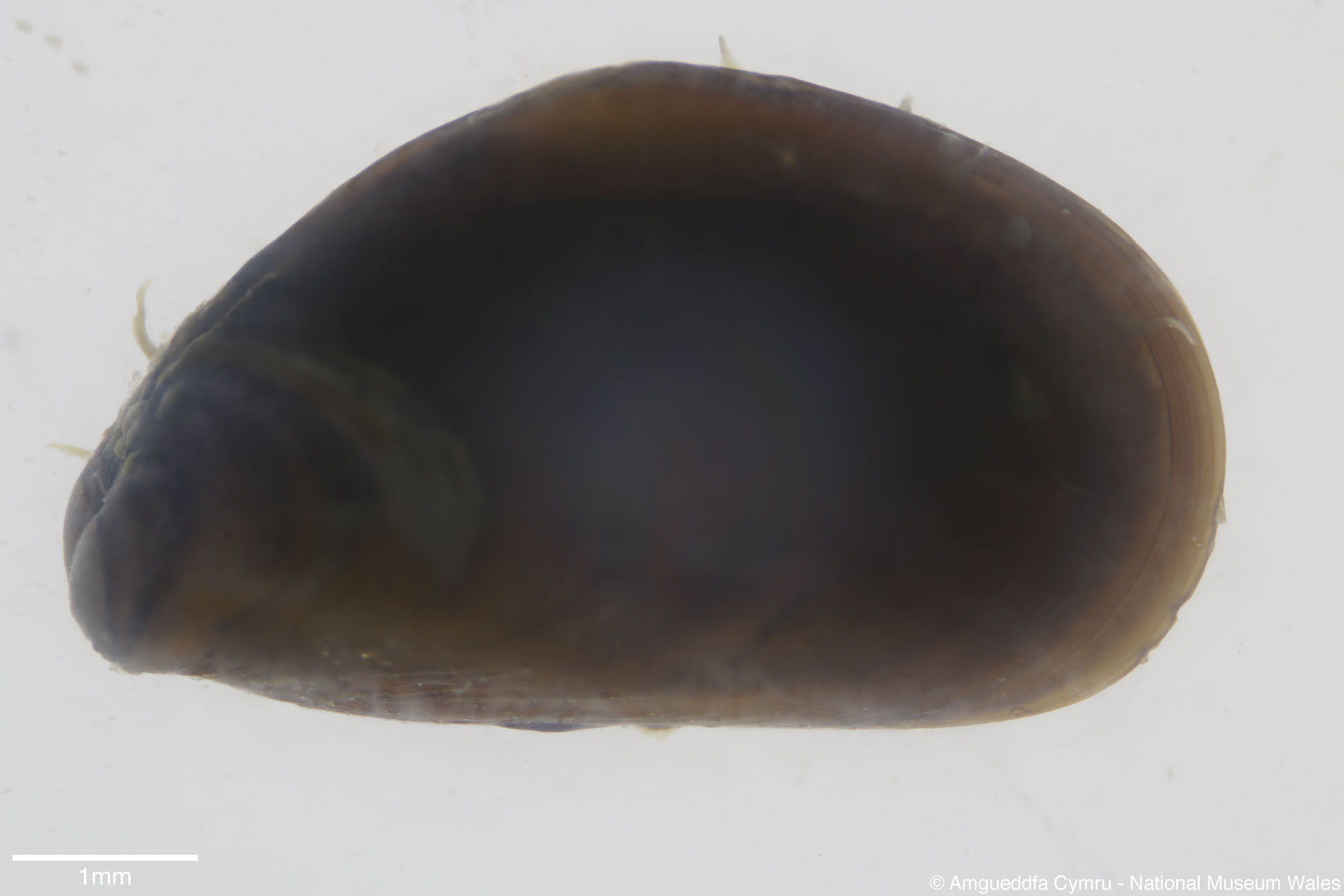
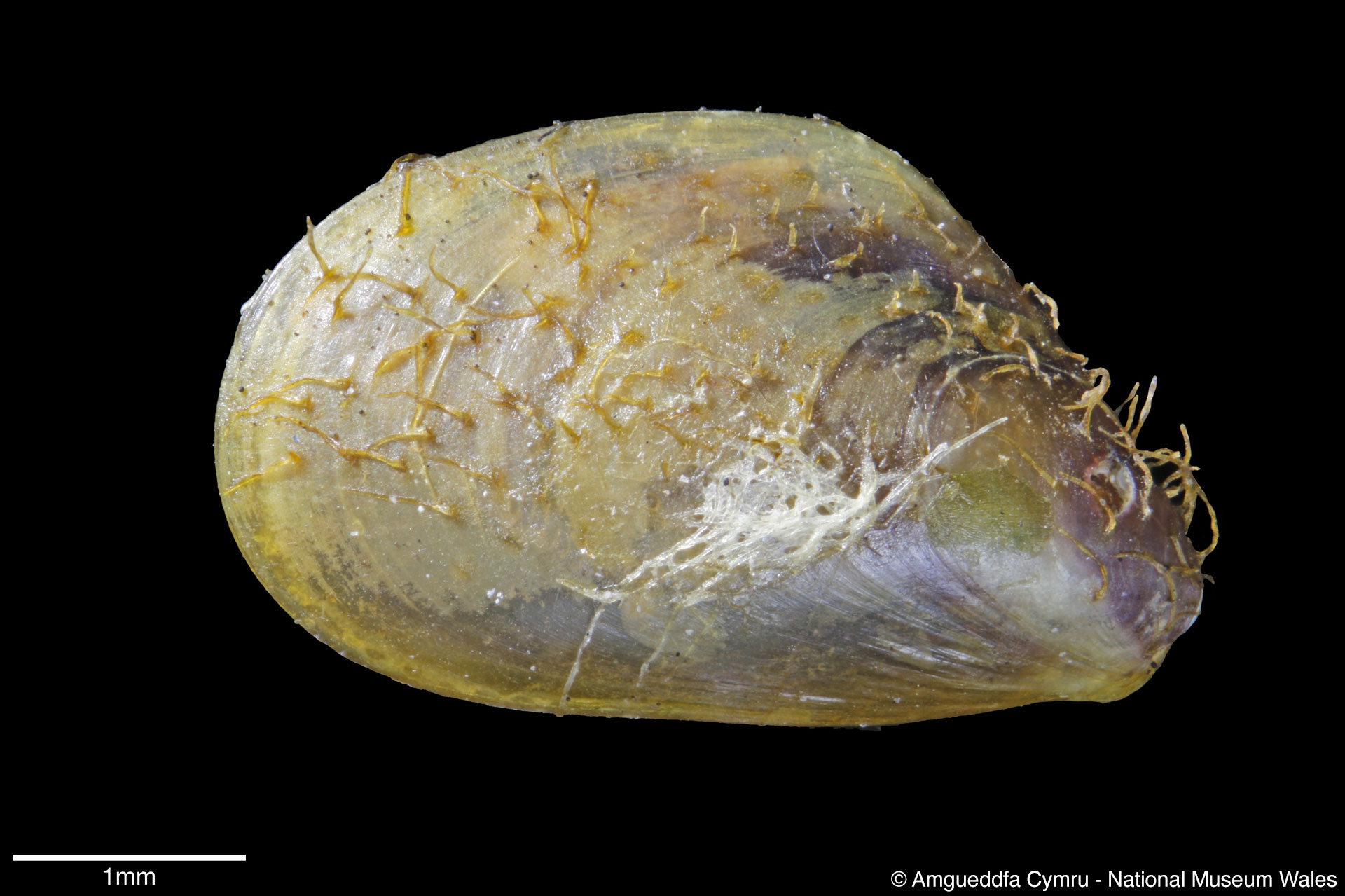
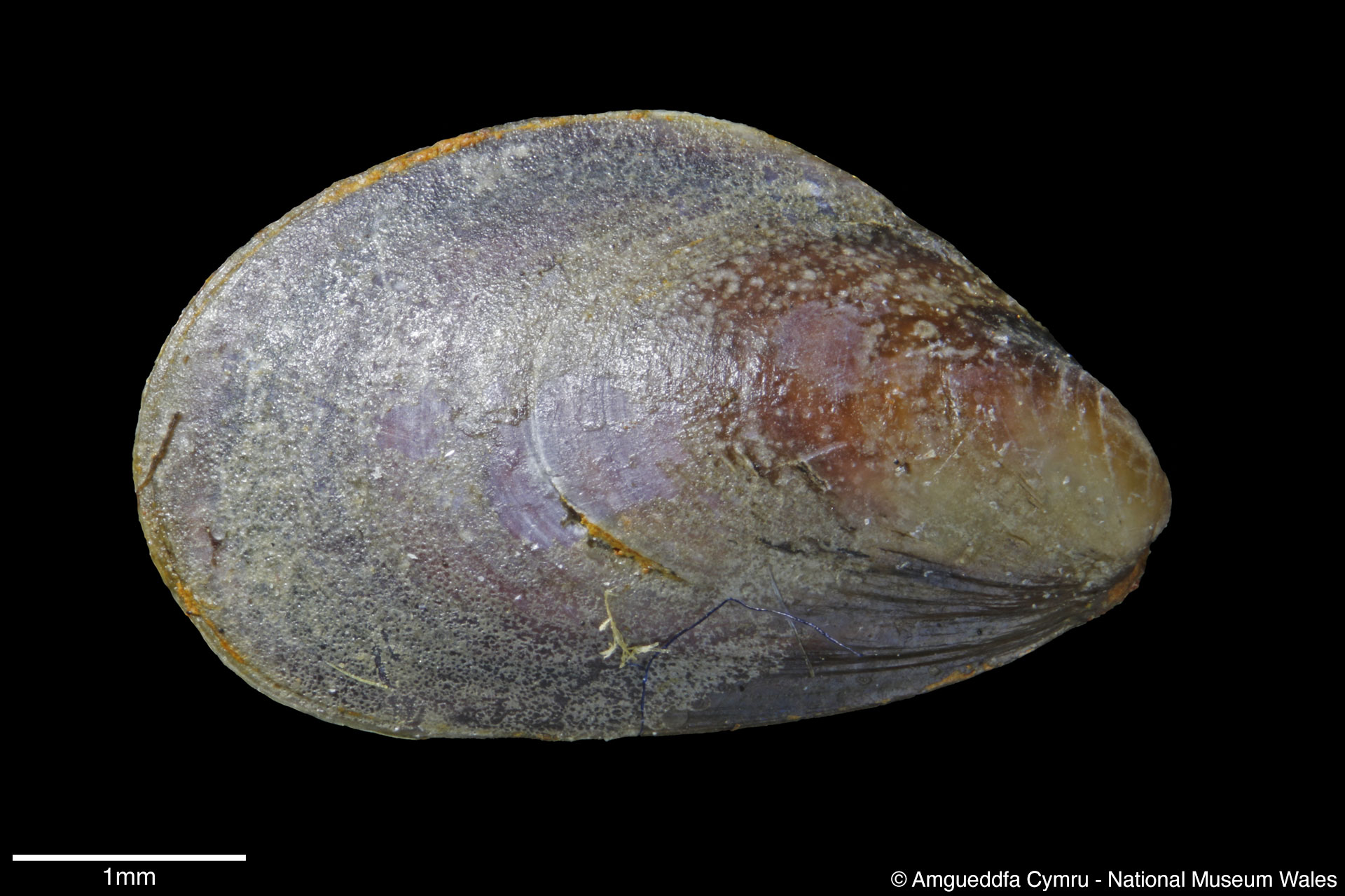
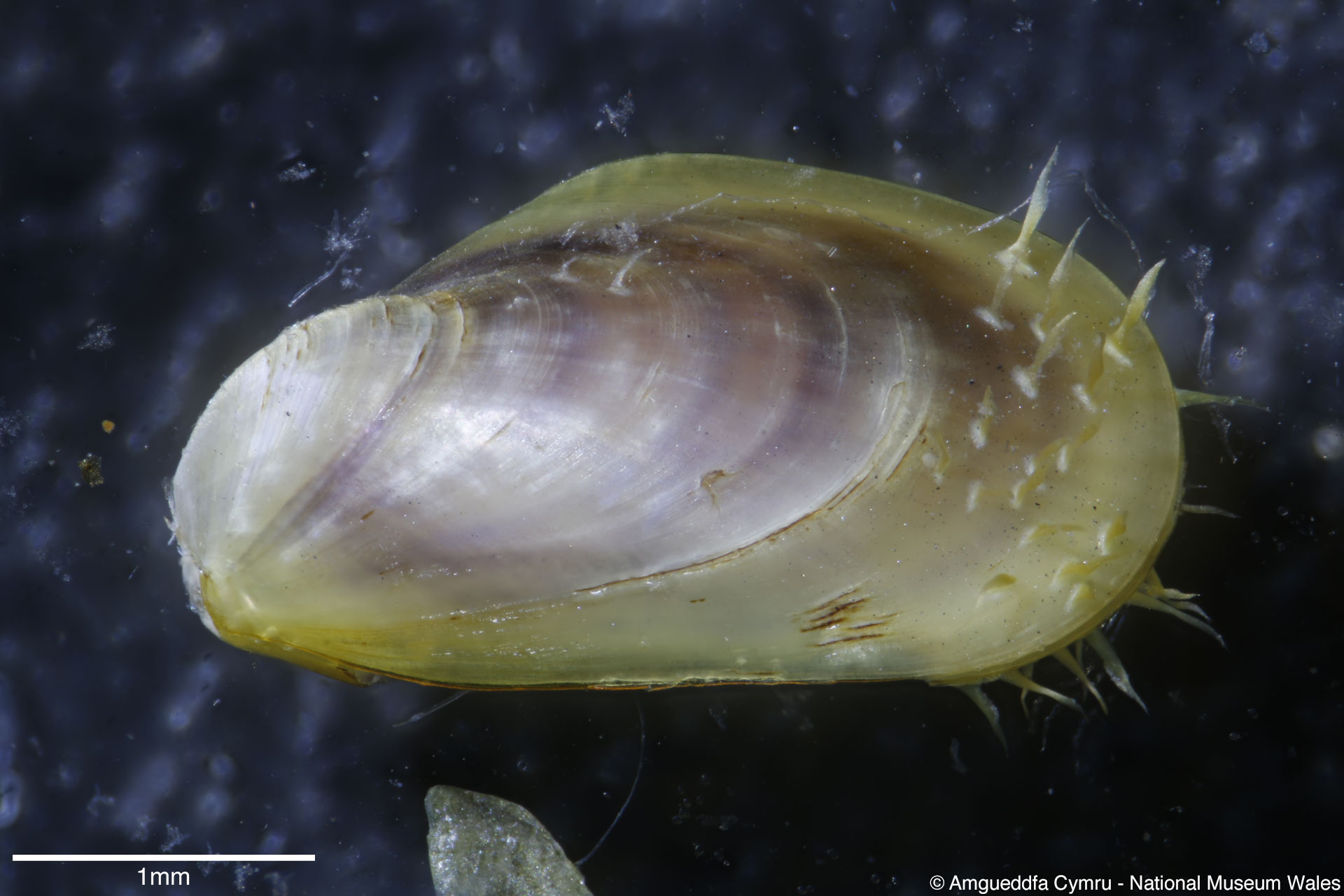
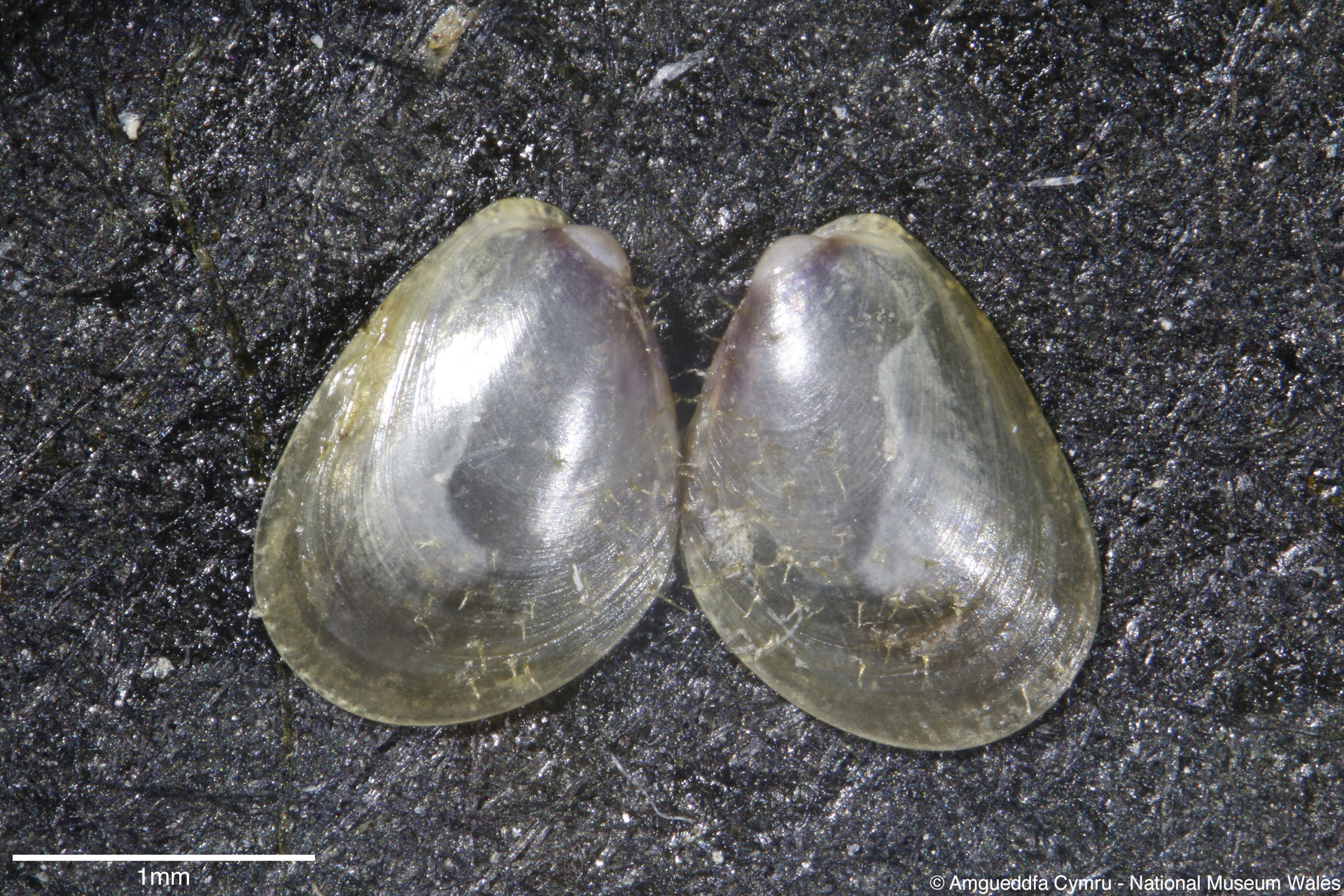
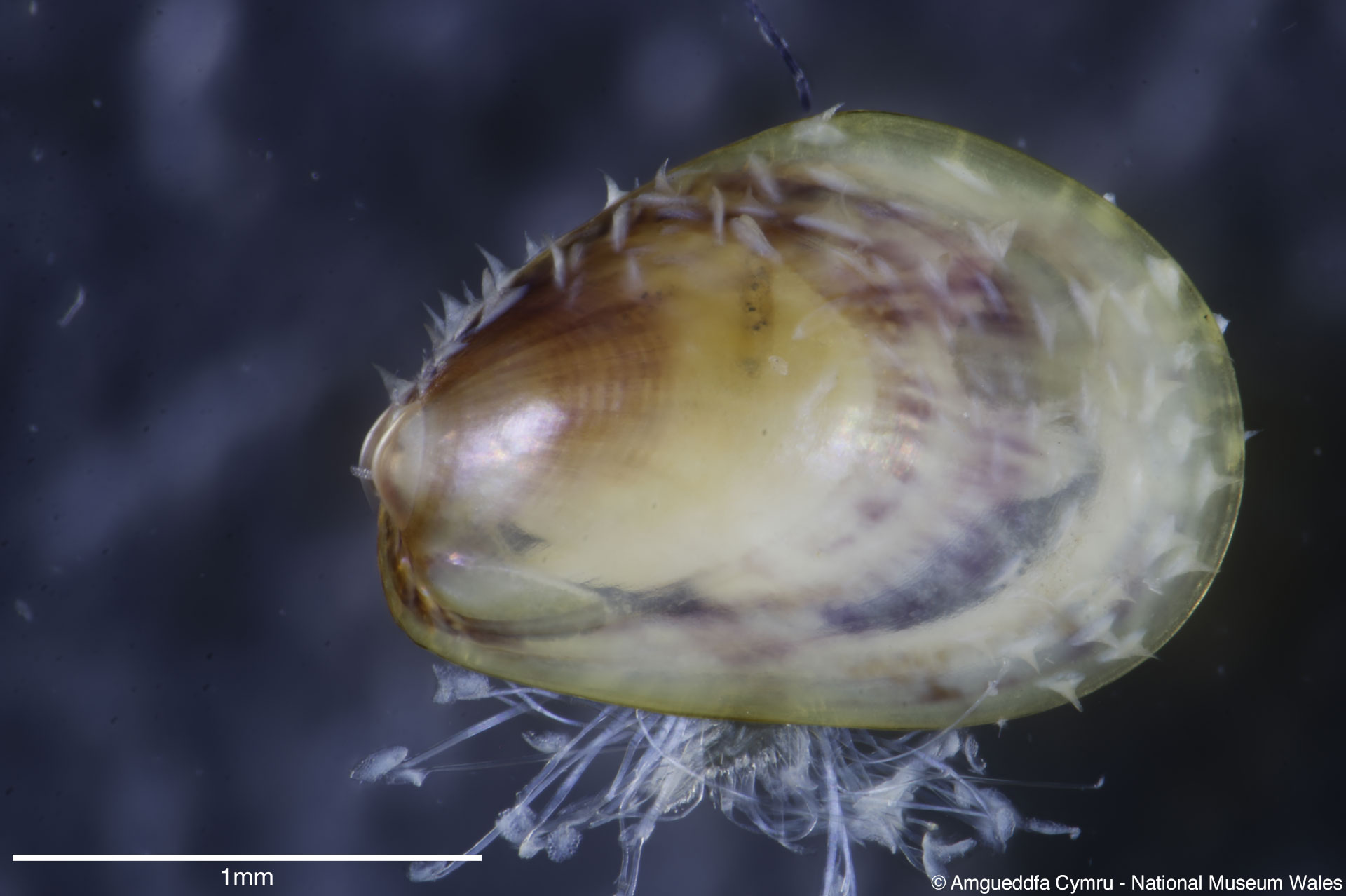
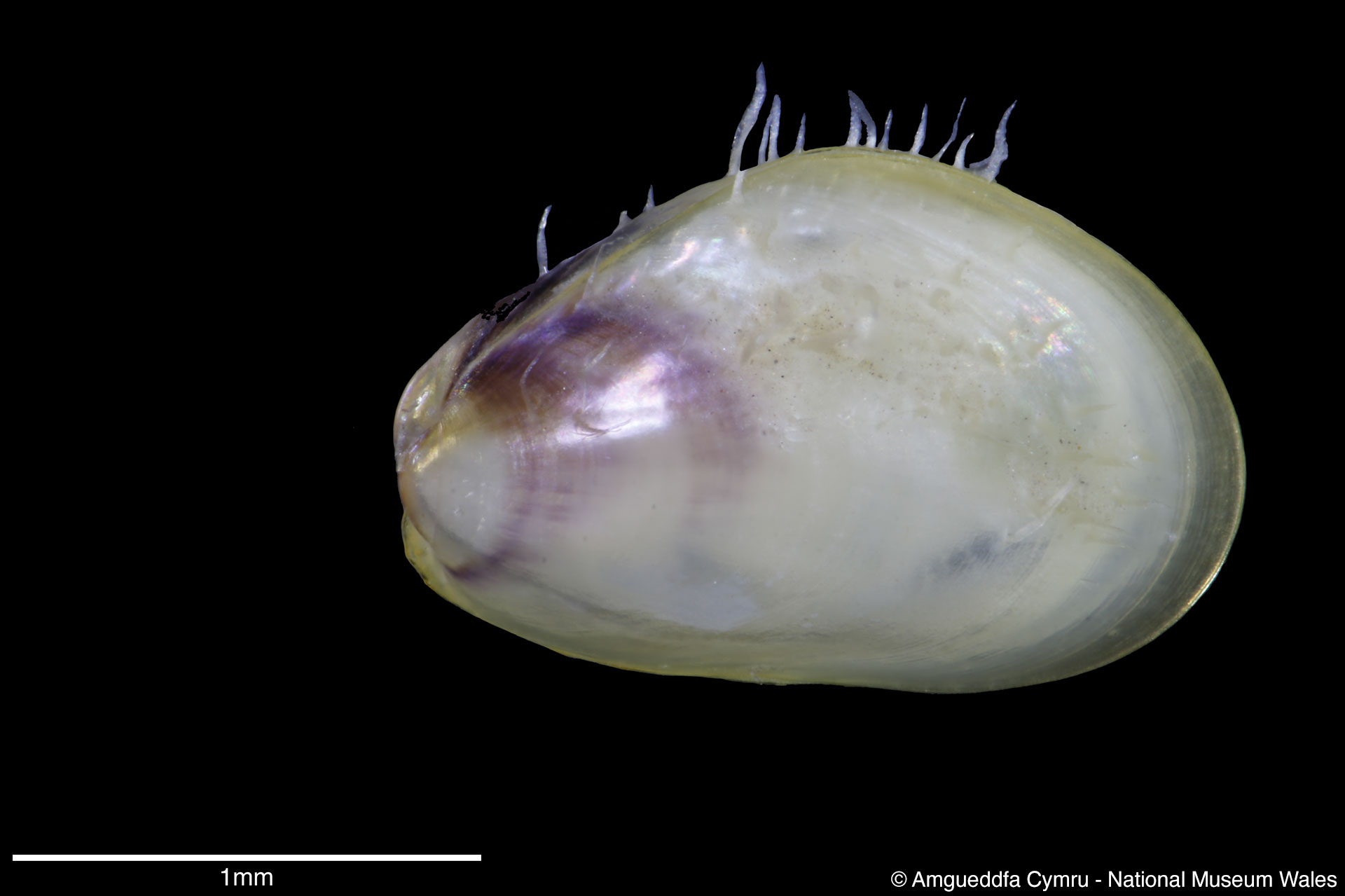
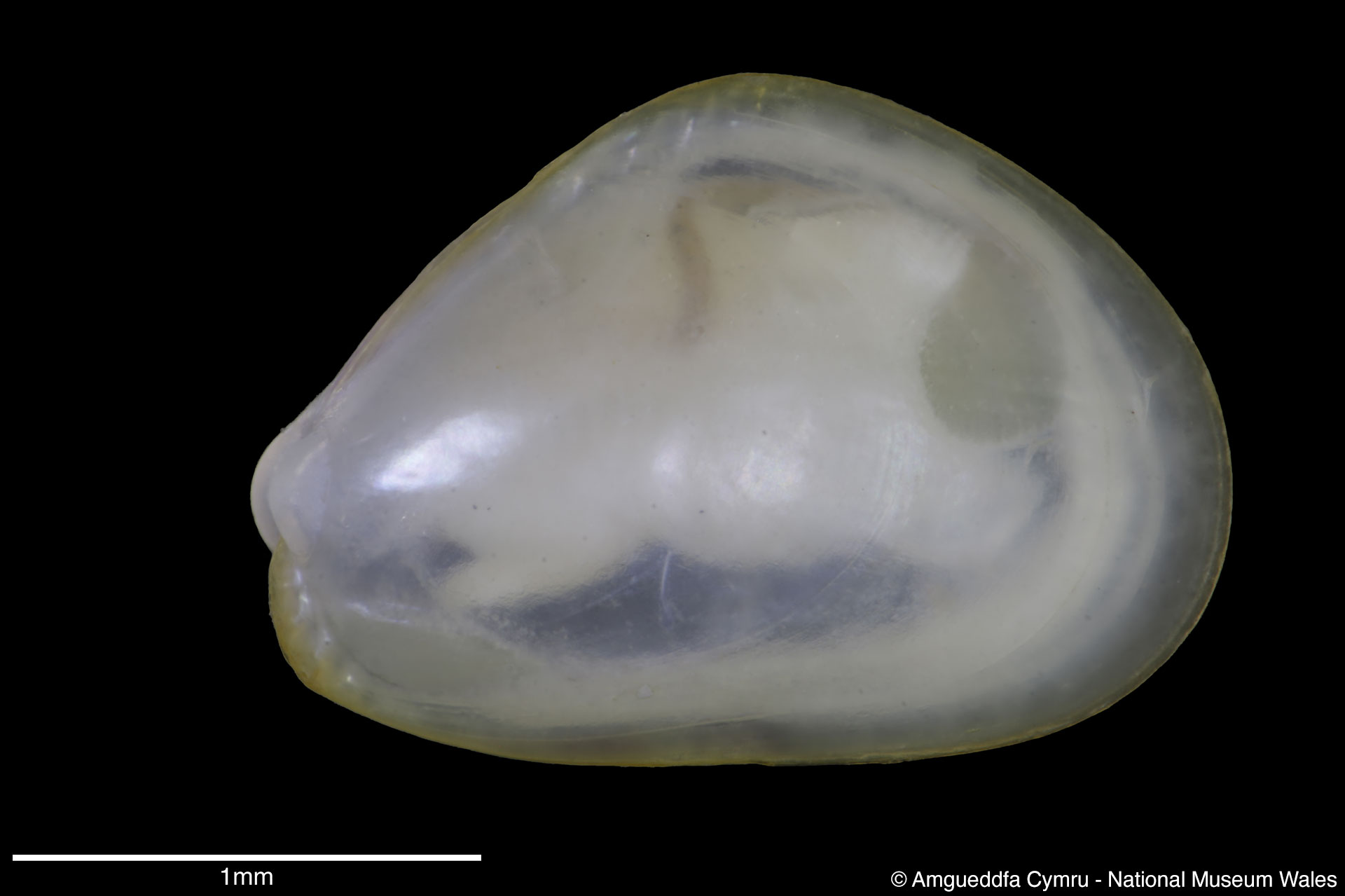
Mytilus edulis Linnaeus, 1758
Mytiloidea : Mytilidae |
| Tebble name: | Mytilus edulis Linnaeus |
| Smith & Heppell name: | Mytilus edulis L.,1758 |
To size: To 150mm. Shell Structure: Thin brittle. Equivalve: Equivalve. Equilateral: Inequilateral, beaks terminal on the anterior end. Outline: Mytiliform, narrowly wedge shaped; ligament margin long, straight sloping gently, posterior dorsal curved and posterior rounded; ventral straight then sloping upward to beaks, not hooked.
Sculpture: Comarginal lines and growth stops. Margin: Inner margin smooth. Ligament: External but sunken, extending 2/3 of ligament margin. Hinge: Smooth except for a few crenulations on the anterior ventral extremity. Pallial Musculature: Cojoined posterior and byssus retractor scar large inset from posterior dorsal margin; anterior adductor scar very small obscure. Periostracum: Thin, persistent, devoid of hairs. Colour: Periostracum blue-black to dark brown, some yellowish with bluish rays. Internal white with margins as external.
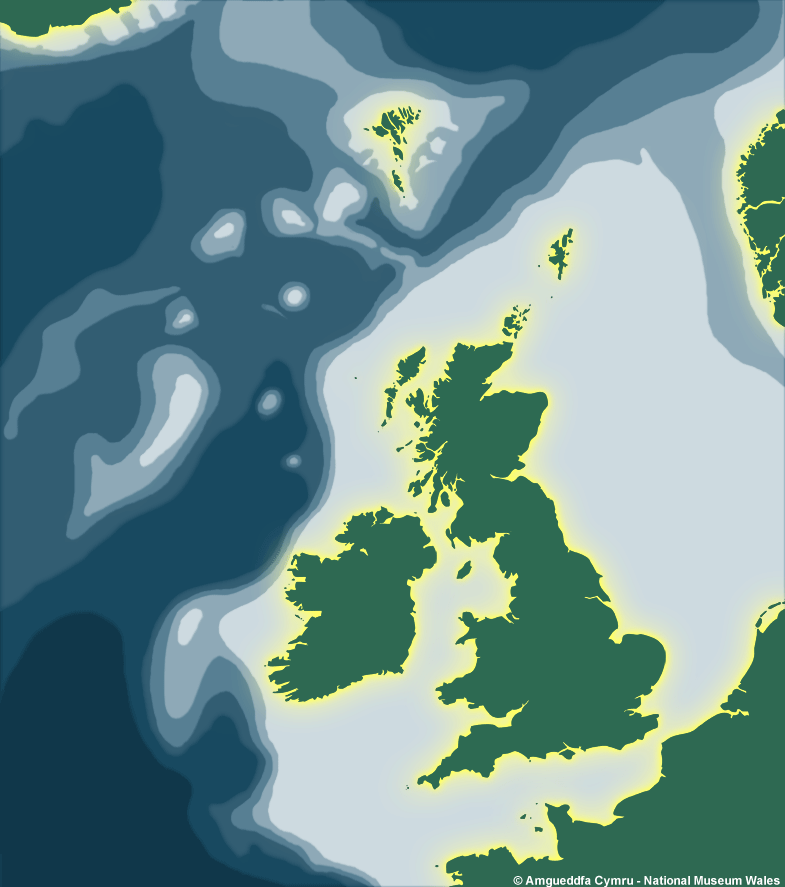
Distribution & Ecology
A review with many references on the Mytilus complex in Europe can be found at http://genimpact.imr.no/__data/page/7650/mussels.pdf.
Also see
Gosling, E. M. 1992. Systematic and geographic distribution of Mytilus. In Gosling, EM editor. The mussel Mytilus: ecology, physiology, genetics and culture. New York Elsevier. pp. 1–17.
Depth Range
Intertidal
Continental Shelf (to 200m)
Additional Information & Related Species
Additional Comments
Related Species
Mytiloidea : Mytilidae
References
Listed are literature citing Mytilus edulis Linnaeus, 1758. Reference containing the species Type Description is highlighted.
|
Bayne B L 1976. Marine mussels; their ecology and physiology no 10. International Biological Programme. Cambridge University Press. 506 pp. |
|
Lewis JR & Seed R 1969. Morphological variations in Mytilus from south-west England in relation to the occurrence of M. galloprovincialis Lmk. Cahiers de biologie marins (Cah. biol. mar.). 10: 231-253. |
|
Linnaeus C 1758. Systema Naturae. Editio decima. 1. Regnum Animale Holmiae, Laurentii Salvii. 824pp. |
|
Seed R 1992. Systematics evolution and distribution of mussels belonging to the genus Mytilus: an overview. American Malacological Bulletin. 9: 123-137. |
|
Verduin A 1979. Conchological evidence for the separate identity of Mytilus edulis L. and M. galloprovincialis Lam.. Basteria. 43: 61-80. |
Resources
- Conchological Society
of Great Britain & Ireland
Provides resources for understanding, identifying, recording, and conserving molluscs - CLEMAM
Check List of European Marine Mollusca - MarLIN
The Marine Life Information Network for Britain and Ireland (MarLIN) provides information for marine environmental management, protection and education. It is a centre of excellence in spatially based and time-series marine biological information and supports good stewardship in the marine environment. - NBN Gateway
National Biodiversity Network's Gateway. Use it to explore UK biodiversity data, as contributed by participating data providers. - BivAToL
- MarBEF
- Malacological Society
- Unitas Malacologica
- Census of Marine Life
- MarBEF
MarBEF, a network of excellence funded by the European Union and consisting of 94 European marine institutes, is a platform to integrate and disseminate knowledge and expertise on marine biodiversity, with links to researchers, industry, stakeholders and the general public.