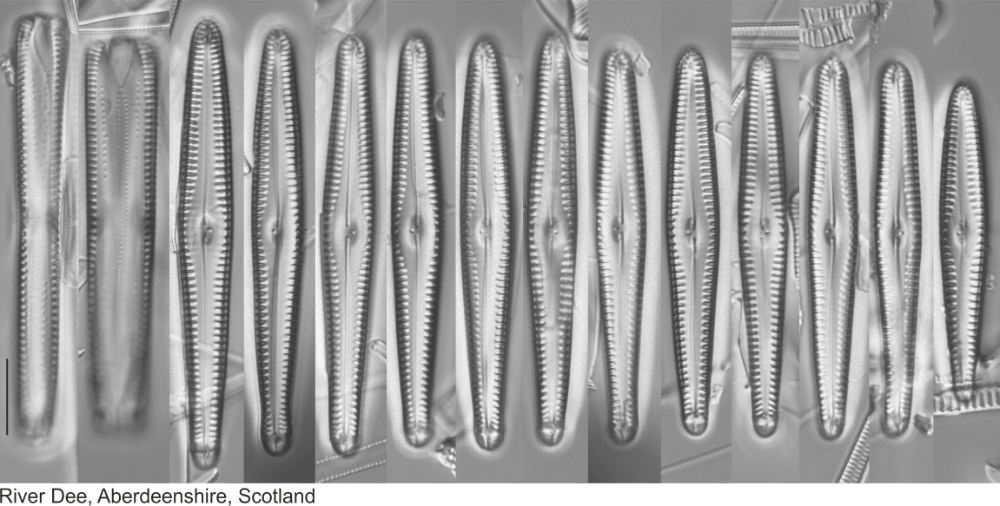
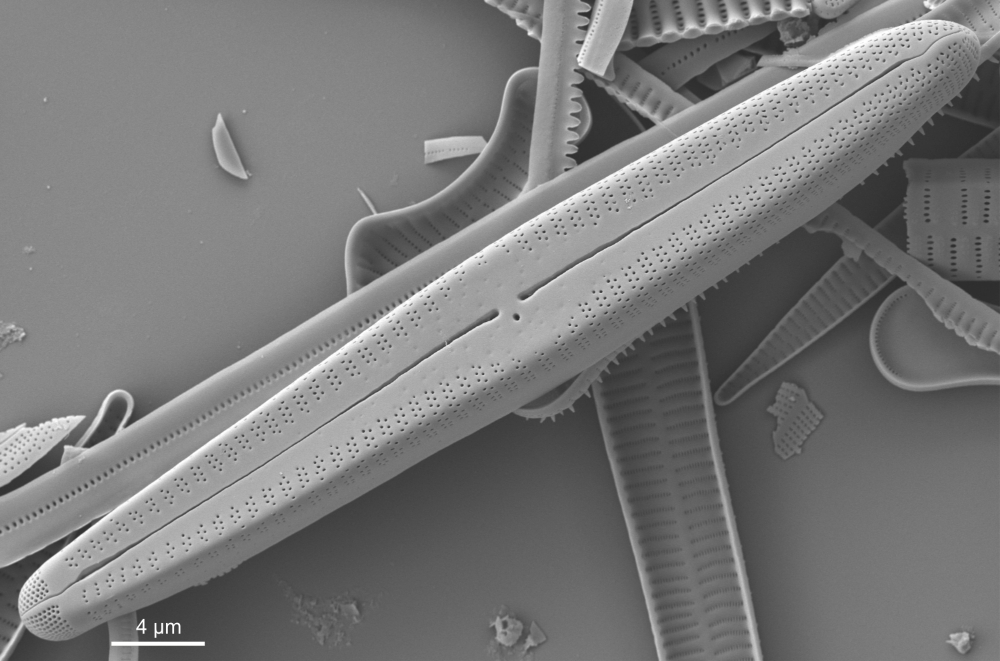
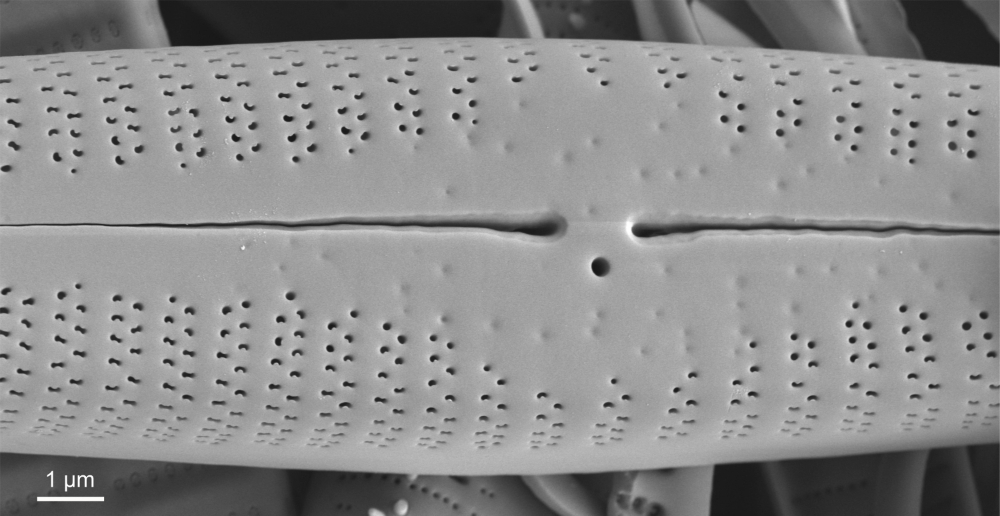
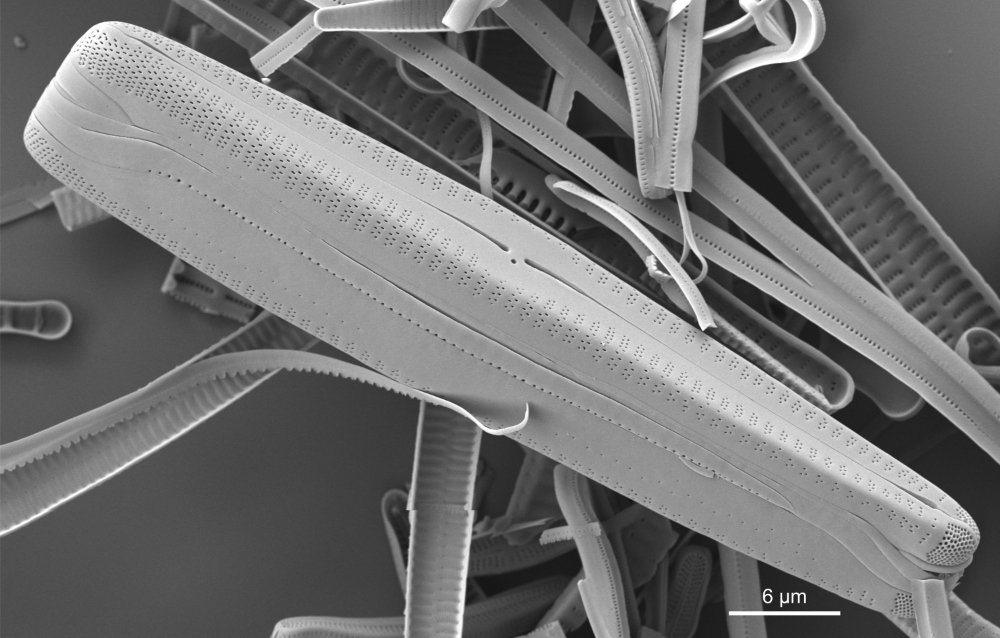
Gomphonema rhombicum Fricke in Schmidt; 1904; pl. 248
Key references
Iserentant R., Ector L. 1996. Gomphonema rhombicum M. Schmidt (Bacillariophyta): typification et description en microscopie optique. Bulletin français de la pêche et de la pisciculture. 341/342: 115-124.
Almeida S.F.P., Craveiro S.C., Calado A.J. 2010. On the identity and distribution in northern Portugal of three Gomphonema species currently misidentified as Gomphonema clevei. Diatom Research. 25(1): 13-27.
Morphology
Length 36-53 µm, width 5.4-7.6 µm (Lange-Bertalot et al. 2017).
Shape
Valves narrow lanceolate with broadly rounded head and foot poles. Frustules in girdle view almost rectangular.
Symmetry
Heteropolar, valve outline bilaterally symmetrical.
Striae
Striae biseriate, slightly radiate throughout the valve, 11-14 in 10 µm.
Central area
Axial area lanceolate widening towards a large rhombic central area.
Raphe
Raphe lateral, proximal raphe ends expanded, internal proximal raphe fissures terminate in small hooks.
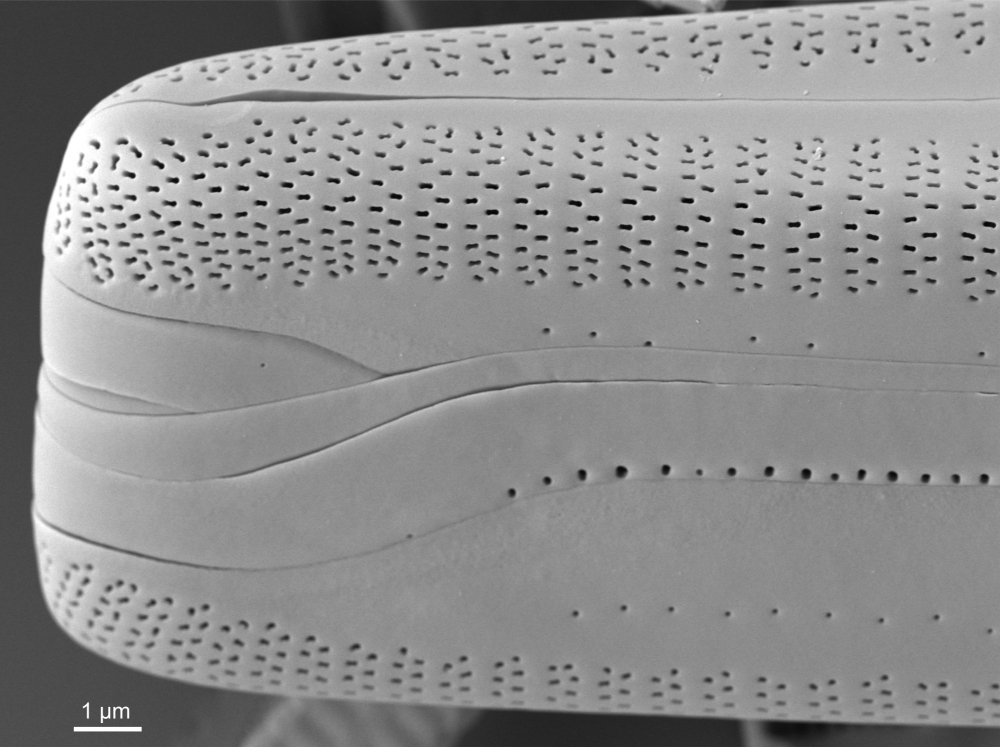
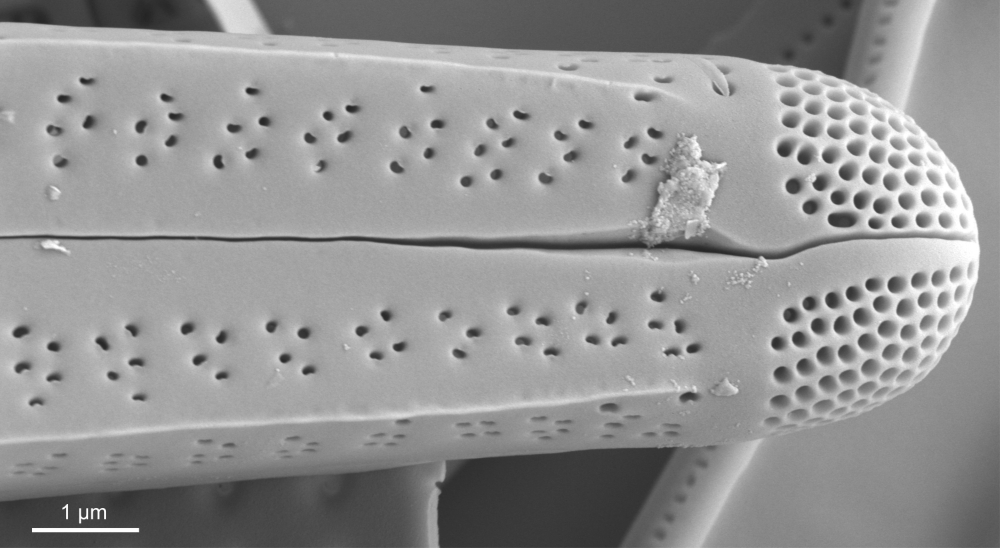
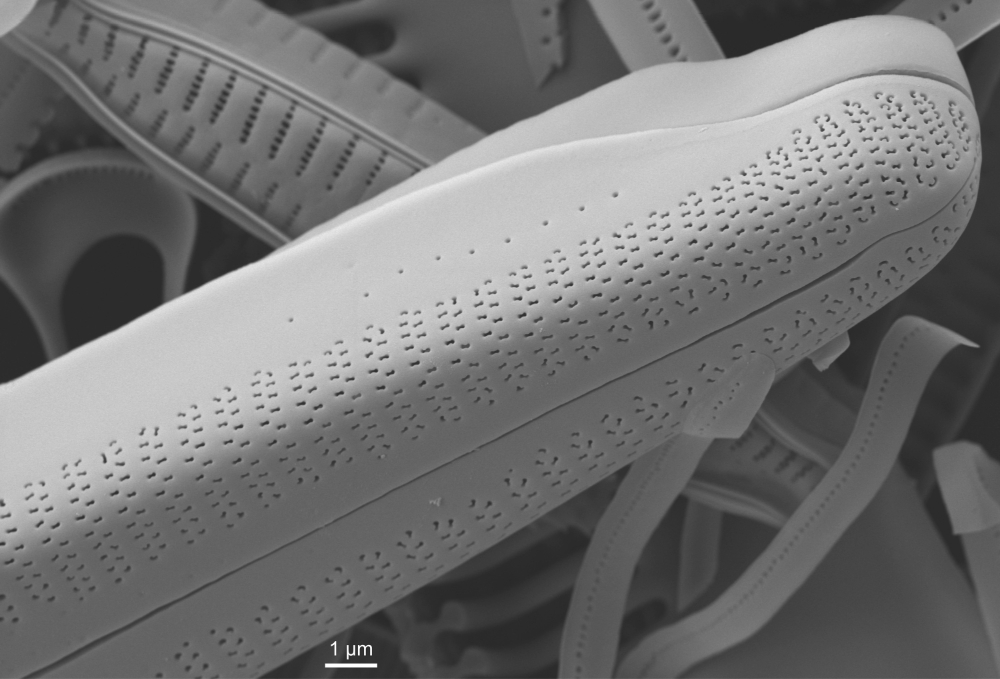
SEM morphology
A single stigma is present with a round external opening and a slit-like internal opening on the side of the central nodule.
Valve mantle with a single row of small pores, interrupted in the centre. Valvocopula with a conspicuous (also in LM) row of larger pores.
Literature
References are given in chronological order.
Reference |
Citation |
|---|---|
| Schmidt A. 1904. Atlas der Diatomaceen-Kunde. Leipzig. O.R. Reisland, Series VI (Heft 62-63): pl. 248 [F. Fricke]. | Type Illustration |
| Iserentant R., Ector L. 1996. Gomphonema rhombicum M. Schmidt (Bacillariophyta): typification et description en microscopie optique. Bulletin français de la pêche et de la pisciculture. 341/342: 115-124. | Morphology; Type Illustration |
| Reichardt E. 2005. Die Identität von Gomphonema entolejum Østrup (Bacillariophyceae) sowie Revision ähnlicher Arten mit weiter Axialarea. Nova Hedwigia. 81(1-2): 115-144. | Morphology; Illustrations |
| Almeida S.F.P., Craveiro S.C., Calado A.J. 2010. On the identity and distribution in northern Portugal of three Gomphonema species currently misidentified as Gomphonema clevei. Diatom Research. 25(1): 13-27. | Morphology; Illustrations; Ecology |
| Lange-Bertalot H., Hofmann G., Werum M., Cantonati M. 2017. Freshwater Benthic Diatoms of Central Europe: Over 800 Common Species Used in Ecological Assessment. Cantonati M., Kelly M.G., Lange-Bertalot H. (eds.), Koeltz Botanical Books, Schmitten-Oberreifenberg, Germany. 942 pp | Morphology; Illustrations; Ecology |
| Pardo I., Delgado C., Abraín R., Gómez-Rodríguez C., García-Roselló E., García L., Reynoldson T.B. 2018. A predictive diatom-based model to assess the ecological status of streams and rivers of Northern Spain. Ecological Indicators. 90: 519-528. | Ecology |
| Quevedo L., Merino K., Godoy S., Carrera C. 2021. Ecological assessment and water quality using benthic diatom communities in an Ecuadorian amazon river. Ecology, Environment and Conservation. 27(1): 152-158. | Ecology |
Similar Species
Similar species not published on this website:
Gomphonema christenseni Lowe & Kociolek; 1984; 471
Gomphonema freesei Lowe & Kociolek; 1984; 472
Gomphonema gandhii Karthick & Kociolek; 2011; 219
Gomphonema incognitum Reichardt, Jüttner & Cox ; 2004; 245-247
Gomphonema moresbyanum E.Reichardt; 2005; 121,122
Gomphonema pararhombicum Reichardt, Jüttner & Cox ; 2004; 238-239