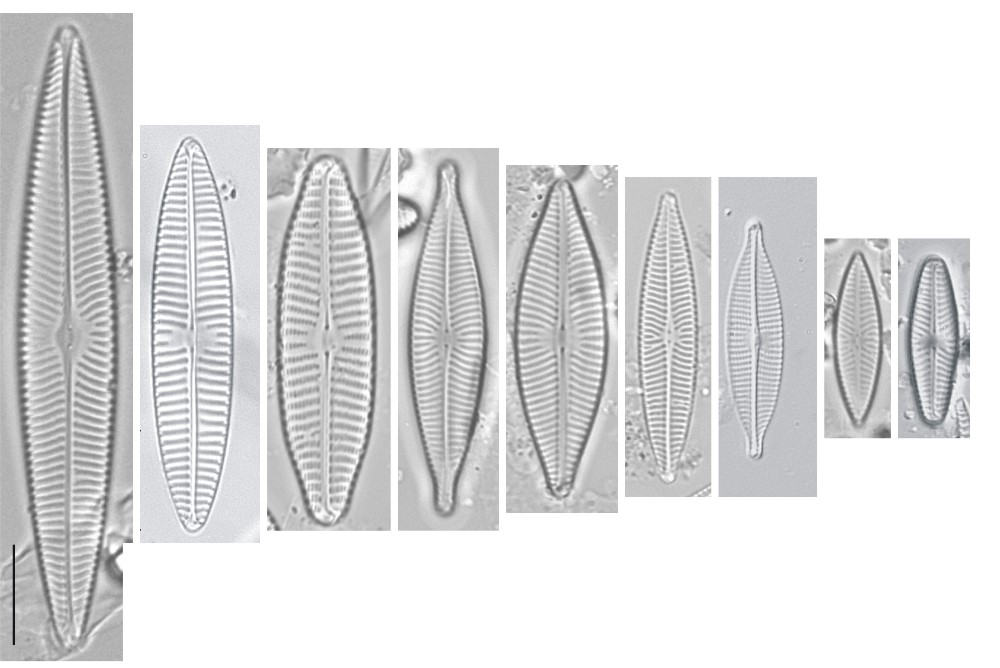
Navicula Bory; 1822; 128
Key references
Cox E.J. 1979. Taxonomic studies on the diatom genus Navicula Bory: The typification of the genus. Bacillaria. 2: 137-153.
Lange-Bertalot H. 2001. Navicula sensu stricto, 10 genera seperated from Navicula sensu lato, Frustulia. 2. Lange-Bertalot H. (ed.), Diatoms of Europe, Diatoms of the European Inland waters and comparable habitats. A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G., Ruggell. 526 pp
Morphology
Frustules lanceolate, linear or linear-elliptical in valve view, with rounded, acute or rostrate poles.
Frustules isovalvar, isopolar and bilaterally symmetrical; cells usually lying in valve view.
Striae uniseriate, parallel or radial; areolae linear, with their long axes at right angles to the striae and aligned to form straight or curved longitudinal lines, occluded by fine pore plates (hymenes) at their inner apertures.
Axial area narrow; internally the raphe sternum usually bears a continuous longitudinal rib on one side of the raphe (the primary side). Central area often developed as a plain circular or rectangular area; it is thickened internally and links with the longitudinal rib borne internally by the raphe sternum.
Raphe straight, straight or hooked endings at the centre externally, simple straight endings at the centre internally, and hooked terminal fissures.
Girdle composed of plain open bands, of which the first is by far the widest.
Two plate-like chloroplasts per cell, one against each side of the girdle, each usually with a single long bar-like pyrenoid (visible in girdle view only).
Frustules isovalvar, isopolar and bilaterally symmetrical; cells usually lying in valve view.
Striae uniseriate, parallel or radial; areolae linear, with their long axes at right angles to the striae and aligned to form straight or curved longitudinal lines, occluded by fine pore plates (hymenes) at their inner apertures.
Axial area narrow; internally the raphe sternum usually bears a continuous longitudinal rib on one side of the raphe (the primary side). Central area often developed as a plain circular or rectangular area; it is thickened internally and links with the longitudinal rib borne internally by the raphe sternum.
Raphe straight, straight or hooked endings at the centre externally, simple straight endings at the centre internally, and hooked terminal fissures.
Girdle composed of plain open bands, of which the first is by far the widest.
Two plate-like chloroplasts per cell, one against each side of the girdle, each usually with a single long bar-like pyrenoid (visible in girdle view only).
Literature
References are given in chronological order.
Reference |
Citation |
|---|---|
| Cox E.J. 1979. Symmetry and valve structure in naviculoid diatoms. Nova Hedwigia Beiheft. 64: 193-206. | Morphology; Illustrations |
| Cox E.J. 1979. Taxonomic studies on the diatom genus Navicula Bory: The typification of the genus. Bacillaria. 2: 137-153. | Morphology; Type Illustration; |
| Krammer K., Lange-Bertalot H. 1985. Naviculaceae Neue und wenig bekannte Taxa, neue Kombinationen und Synonyme sowie Bemerkungen zu einigen Gattungen. 9. Bibliotheca Diatomologica. 230 pp | Morphology; Illustrations |
| Cox E.J. 1999. Studies on the diatom genus Navicula Bory. VIII. Variation in valve morphology in relation to the generic diagnosis based on Navicula tripunctata (O.F. Müller) Bory. Diatom Research. 14(2): 207-237. | Morphology; Illustrations |
| Lange-Bertalot H. 2001. Navicula sensu stricto, 10 genera seperated from Navicula sensu lato, Frustulia. 2. Lange-Bertalot H. (ed.), Diatoms of Europe, Diatoms of the European Inland waters and comparable habitats. A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G., Ruggell. 526 pp | Morphology; Taxonomy; Illustrations |
| Lange-Bertalot H., Witkowski A., Bogaczewicz-Adamczak B., Zgrundo A. 2003. Rare and new small-celled taxa of Navicula s. str. in the Gulf of Gdansk and in its freshwater affluents. Limnologica. 33: 258-270. | Morphology; Illustrations |
| Metzeltin D., Lange-Bertalot H. 2007. Tropical diatoms of South America II. Special remarks on biogeography disjunction. Iconographia Diatomologica, Vol. 18., Annotated Diatom Micrographs. Diversity-Taxonomy-Biogeography. H. Lange-Bertalot (ed.), A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G. 877 pp | Morphology; Illustrations |
| Kulikovskiy M.S., Lange-Bertalot H., Metzeltin D., Witkowski A. 2012. Lake Baikal: hotspot of endemic diatoms I. Iconographia Diatomologica Lange-Bertalot, H. (Ed), Vol. 23, A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G., Ruggell. 607 pp | Illustrations; Morphology; Taxonomy |
| Potapova M. 2013. The types of 22 Navicula (Bacillariophyta) species described by Ruth Patrick. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 162: 1-23. | Morphology; Illustrations; Taxonomy |
This page should be cited as:
Mann D. G. Navicula Bory; 1822; 128. In: Jüttner I., Carter C., Cox E.J., Ector L., Jones V., Kelly M.G., Kennedy B., Mann D.G., Turner J. A., Van de Vijver B., Wetzel C.E., Williams D.M..
Freshwater Diatom Flora of Britain and Ireland. Amgueddfa Cymru - National Museum Wales. Available online at https://naturalhistory.museumwales.ac.uk/diatoms/browsespecies.php?-recid=3722. [Accessed:
].
Record last modified: 27/12/2020