| Apical pore field (APF) |
An area of smaller, unoccluded pores at one or both apices of the valve, distinguishable from the striae primarily by pore size and arrangement, usually indicating potential attachment to surfaces by mucilaginous pads or stalks.
Reichardt E. 1999. Zur Revision der Gattung Gomphonema. Die Arten um G. affine/insigne, G. angustatum/micropus, G. acuminatum sowie gomphonemoide Diatomeen aus dem Oberoligozän in Böhmen. Iconographia Diatomologica, Vol. 8, Koeltz Scientific Books, A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, Ruggell. 203 pp
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Notes: The form of the pore field varies with taxa. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 External view of apical pore field in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
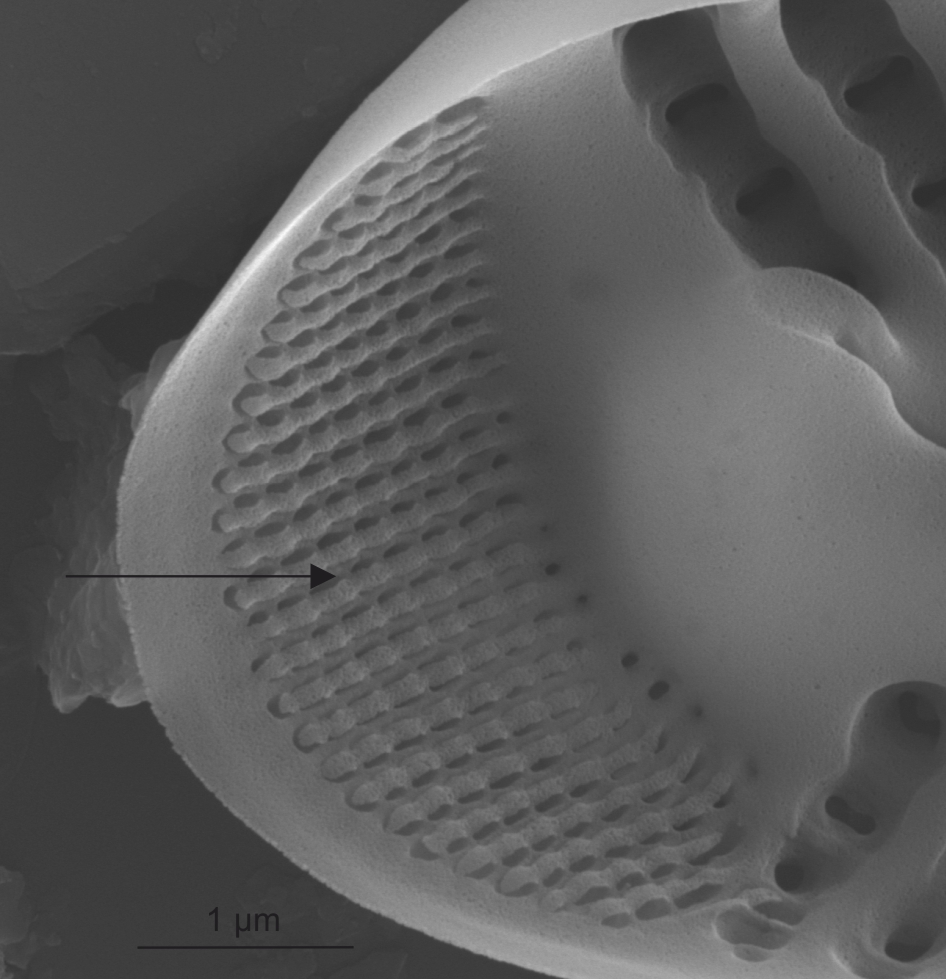 Internal view of apical pore field in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
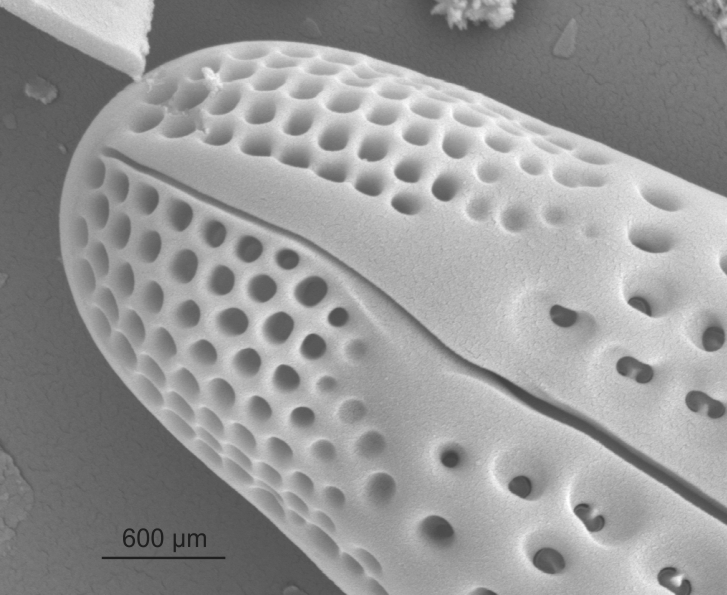 External view of apical pore field in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Apical pore field: bisected |
Area of small unoccluded pores at the apex of a valve bisected by the terminal raphe fissures and distinguishable from the striae primarily by pore size and arrangement.
Kociolek J.P., Woodward J., Graeff C. 2016. New and endemic Gomphonema C.G. Ehrenberg (Bacillariophyceae) species from Hawaii. Nova Hedwigia. 102(1-2): 141-171.
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 External view of bisected apical pore field in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Apical pore field: non-bisected |
Apical pore field clearly separated from the striae by the deflected terminal raphe fissure.
Krammer K. 2002. Cymbella. Lange-Bertalot H. (ed), Diatoms of Europe, Diatoms of the European Inland Waters and Comparable Habitats, Vol.3, A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G., Ruggell. 584 pp
Notes: See in dorsiventral taxa such as some species in Cymbella. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
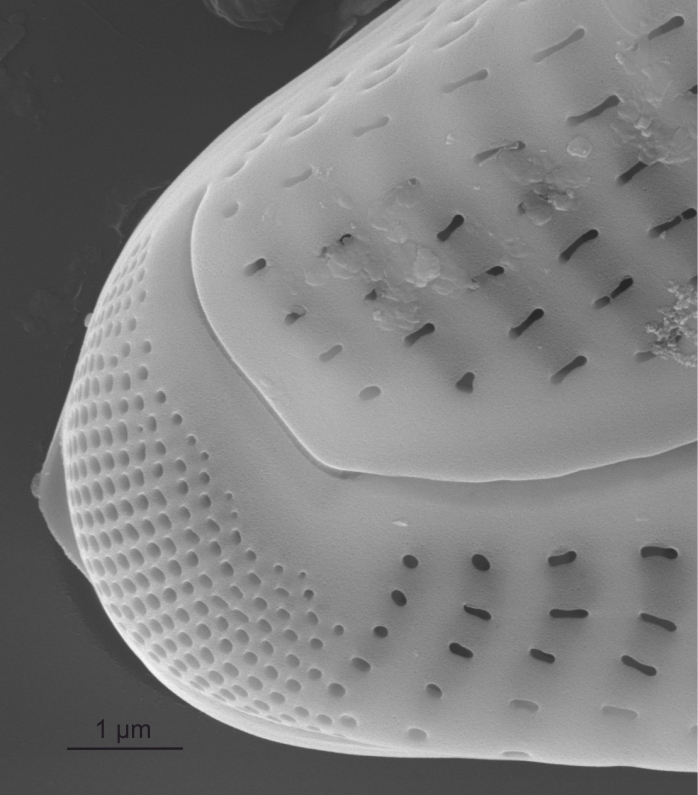 External view of non-bisected apical pore field in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Areola / areolae |
Pores in the valve closed by a single occlusion, which may be at the external or internal surface, or midway between external and internal surfaces.
Cox E.J., Ross R. 1981. The Striae of Pennate Diatoms. Proceedings of the 6th Diatom Symposium on Recent and Fossil Diatoms. (ed. R Ross). 267-278 pp
Cox E.J. 2004. Pore occlusions in raphid diatoms - a reassessment of their structure and terminology, with particular reference to members of the Cymbellales. Diatom. 20: 33-46.
Anonymous. 1975. Proposals for standardization of diatom terminology and diagnoses. 53. Nova Hedwigia, Beihefte. 323-354 pp
Notes: Form of occlusion varies across taxa. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Areolae in Didymosphenia (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
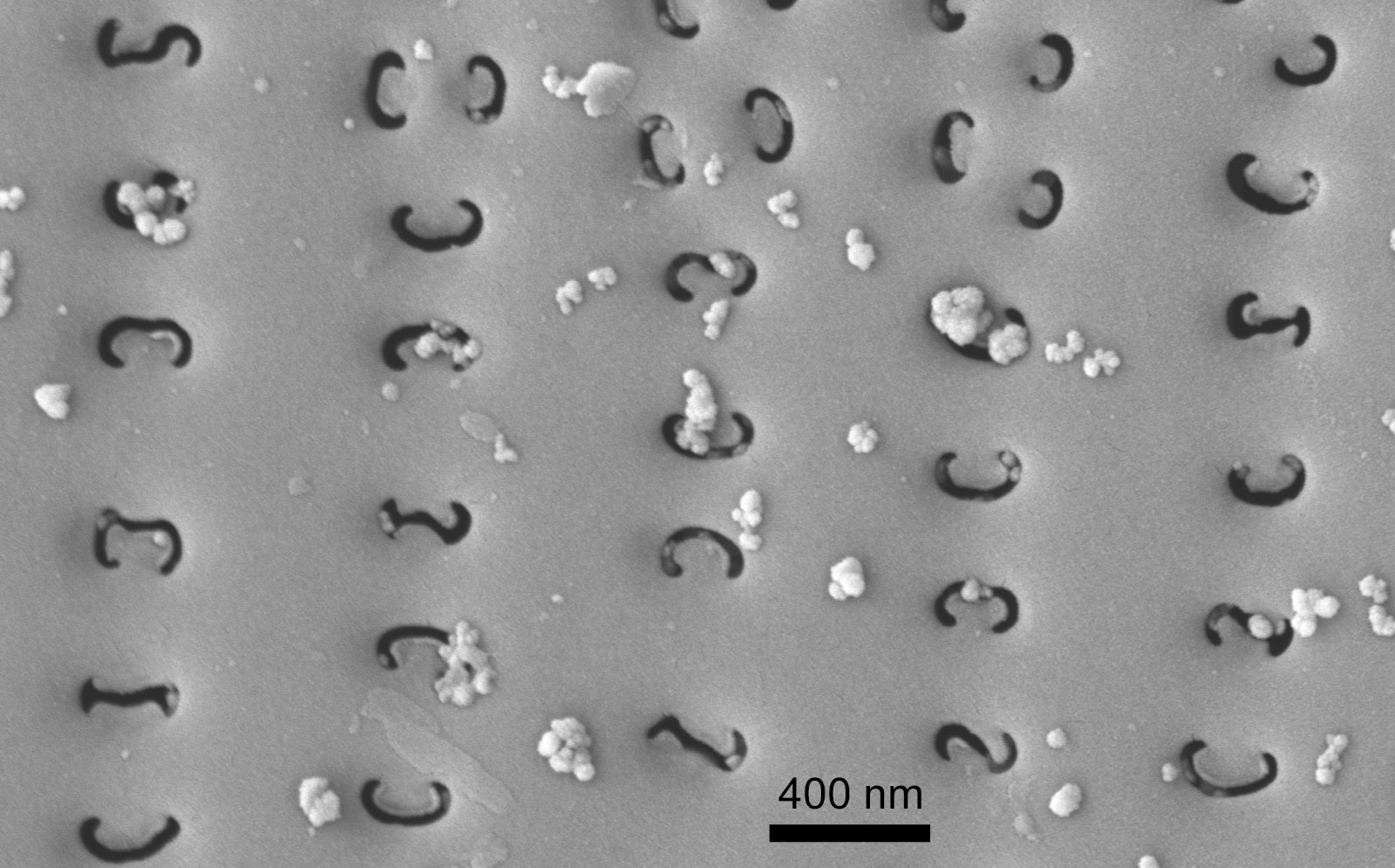 Variously curved external areola openings in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Lineolate areolae in Navicula (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Variously shaped external areola openings in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Axial area |
Areas without ornamentation flanking the raphe slits.
Barber H.G., Haworth E.Y. 1981. A Guide to the Morphology of the Diatom Frustule. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside. 112 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Axial area in Navicula (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
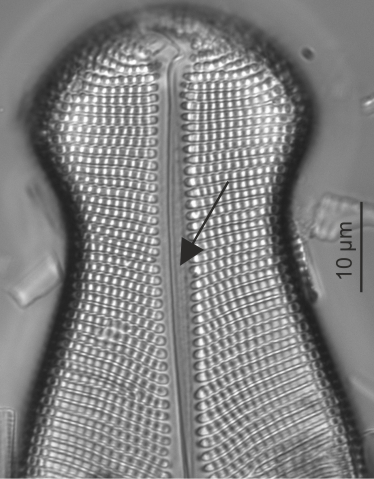 Axial area in Didymosphenia (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Cavum |
Area without ornamentation to one side of the centre of the valve, with a hooded internal overgrowth, distinguishable in LM by its curved margin some distance from the valve margin.
Wetzel C.E., Van de Vijver B., Blanco S., Ector L. 2019. On some common and new cavum-bearing Planothidium (Bacillariophyta) species from freshwater. Fottea, Olomouc. 19(1): 50-89.
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
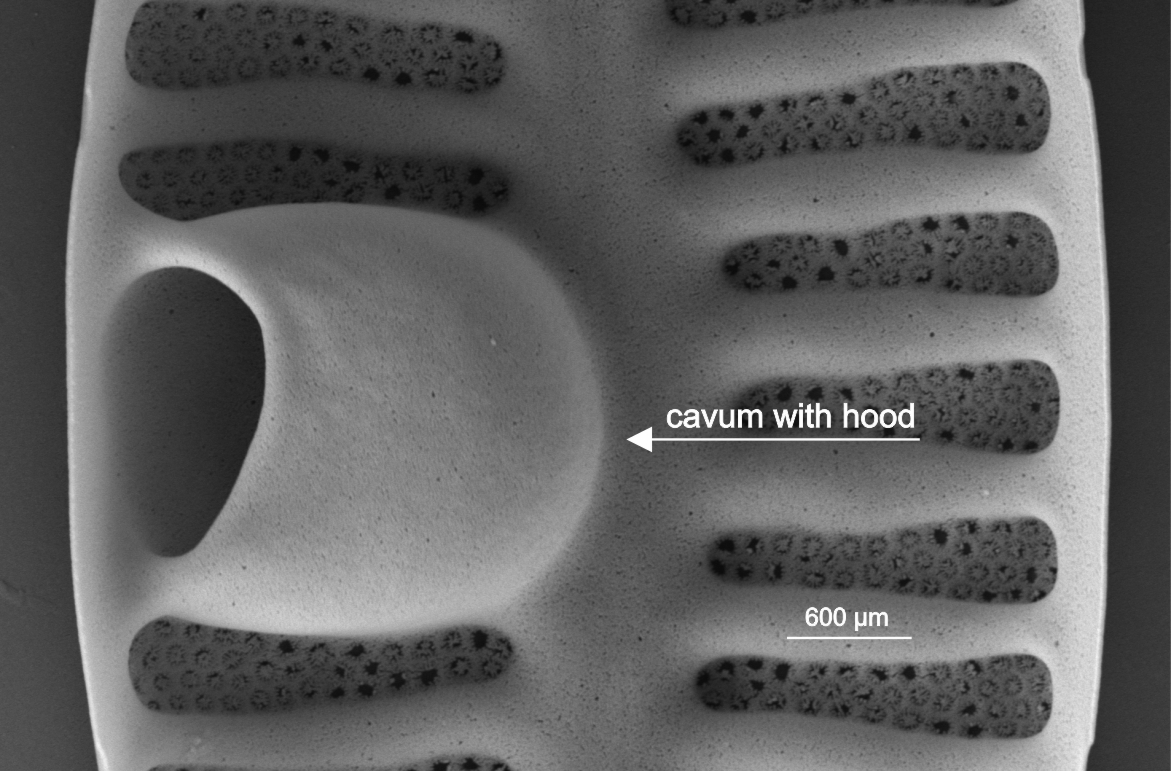 Internal view of cavum in Planothidium (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Central area |
Area at centre of valve, between the central raphe endings and the central striae.
Barber H.G., Haworth E.Y. 1981. A Guide to the Morphology of the Diatom Frustule. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside. 112 pp
Notes: Central area shape is often species specific. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
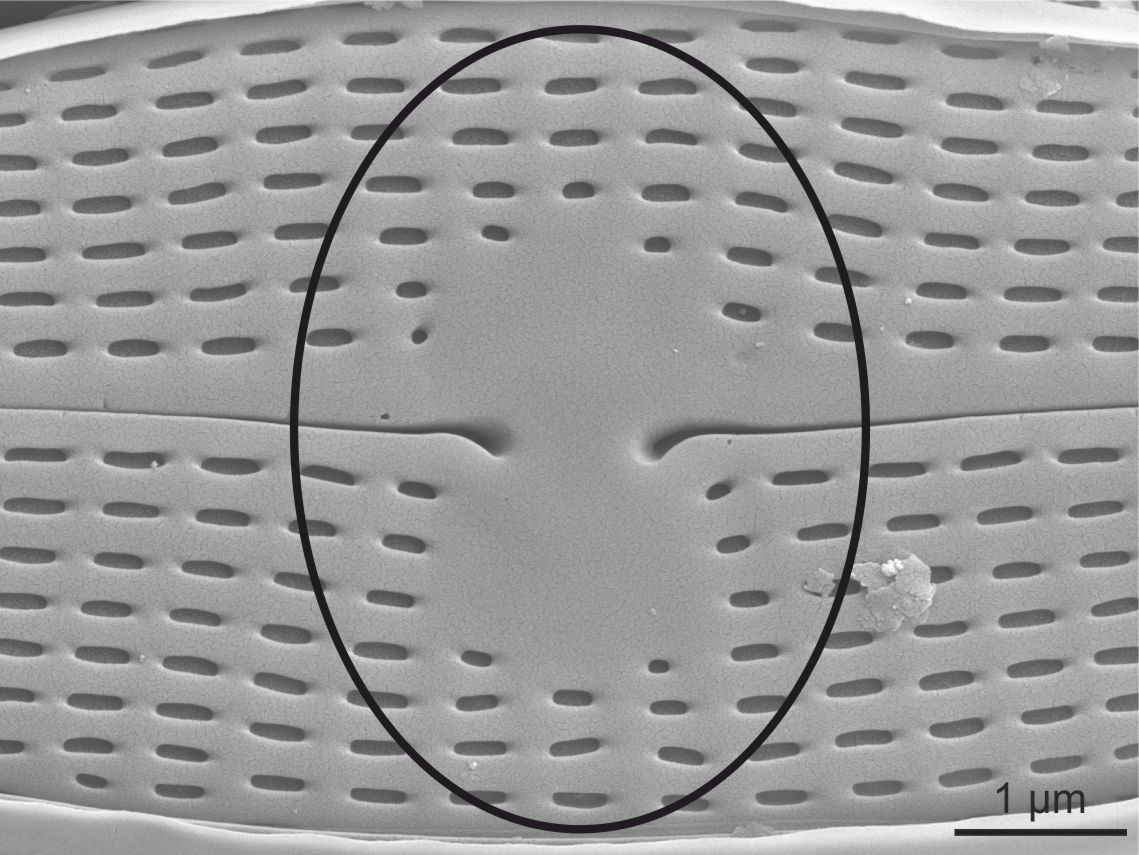 External view of central area in Navicula (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Central nodule |
Internally thickened region between the central raphe endings.
Cox E.J. 1999. Variation in patterns of valve morphogenesis between representatives of six biraphid diatom genera (Bacillariophyceae). Journal of Phycology. 35: 1297-1312.
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
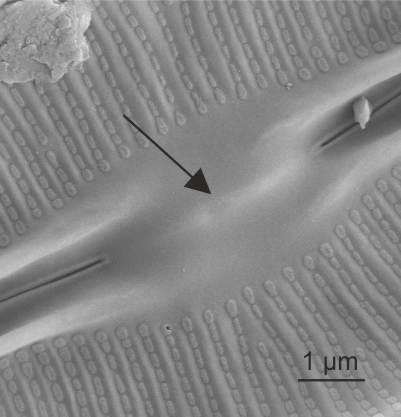 Central nodule in Frustulia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
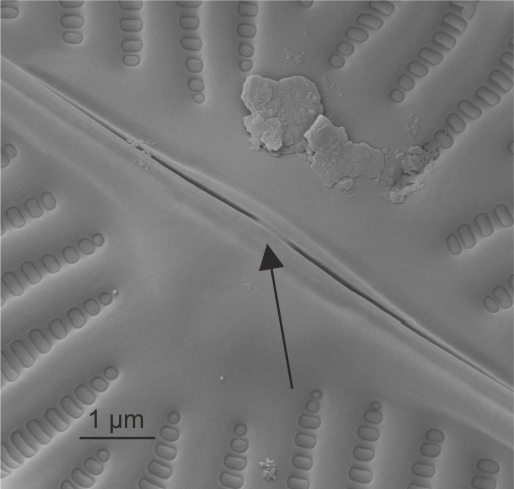 Central nodule in Navicula (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Fascia |
Area without ornamentation traversing the centre of the valve, usually not noticeably thicker than the virgae, if on one side of the valve only then termed unilateral.
Cleve P.T. 1895. Synopsis of the Naviculoid Diatoms, Part II. Kongliga Svenska-Vetenskaps Akademiens Handlingar. 27(3): 1-219; 4 pls.
Cox E.J. 2001. What constitutes a stauros? A morphogenetic perspective. Gantner, Ruggell.
Cox E.J. 1999. Variation in patterns of valve morphogenesis between representatives of six biraphid diatom genera (Bacillariophyceae). Journal of Phycology. 35: 1297-1312.
Barber H.G., Haworth E.Y. 1981. A Guide to the Morphology of the Diatom Frustule. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside. 112 pp
Notes: Shadow lines or ghost striae may sometimes be visible in a fascia. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Fascia in Ulnaria (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 External view of fascia in Pinnularia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Fibula / fibulae |
Struts of silica spanning the raphe slits of keeled raphid diatoms internally.
Paddock T.B.B., Sims P.A. 1977. A preliminary survey of the raphe structure of some advanced groups of diatoms. Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft. 54: 291-322.
Paddock T.B.B., Sims P.A. 1981. A morphological study of keels of various raphe-bearing diatoms. Bacillaria. 4: 177-222.
Mann D.G . 1977. The diatom genus Hantzschia Grunow: an appraisal. Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft. 54: 323-354.
Notes: Seen e.g. in Nitzschia, Hantzschia, Denticula, Surirella, Campylodiscus, Cymatopleura. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Fibulae in Nitzschia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
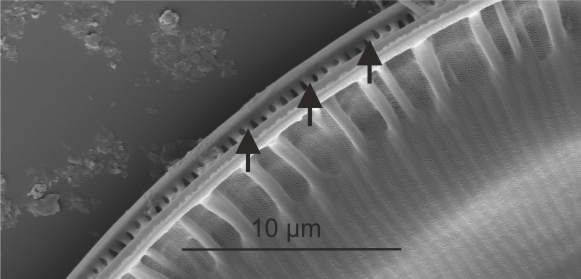 Fibulae in Surirella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Frustule |
The entire siliceous components of the cell wall of a diatom (comprising two valves, epivalve + hypovalve, and their linking girdle bands; i.e. epitheca + hypotheca).
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Frustule in Odontidium (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
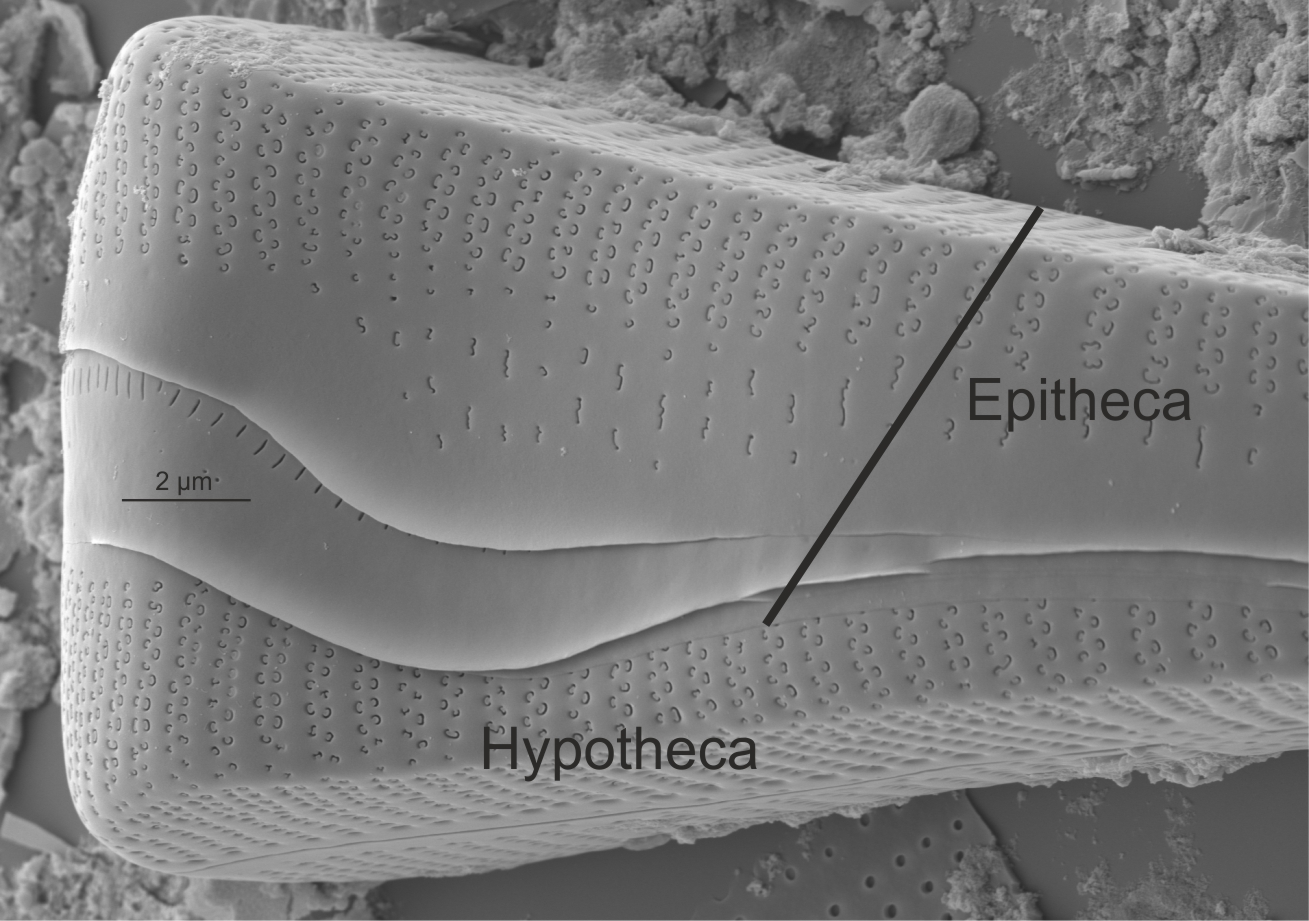 Epitheca and hypotheca in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Girdle band: copula / copulae |
An element of the cingulum, in the form of a split or entire band, or a shorter band-like element (half-band or end plate).
Barber H.G., Haworth E.Y. 1981. A Guide to the Morphology of the Diatom Frustule. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside. 112 pp
Notes: Girdle bands may have pores or be pore free; margins of the valvocopula (first formed band adjacent to the valve) may be undulate where they abut the valve. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Entire girdle view of Eunotia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Entire girdle view of Cocconeis (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
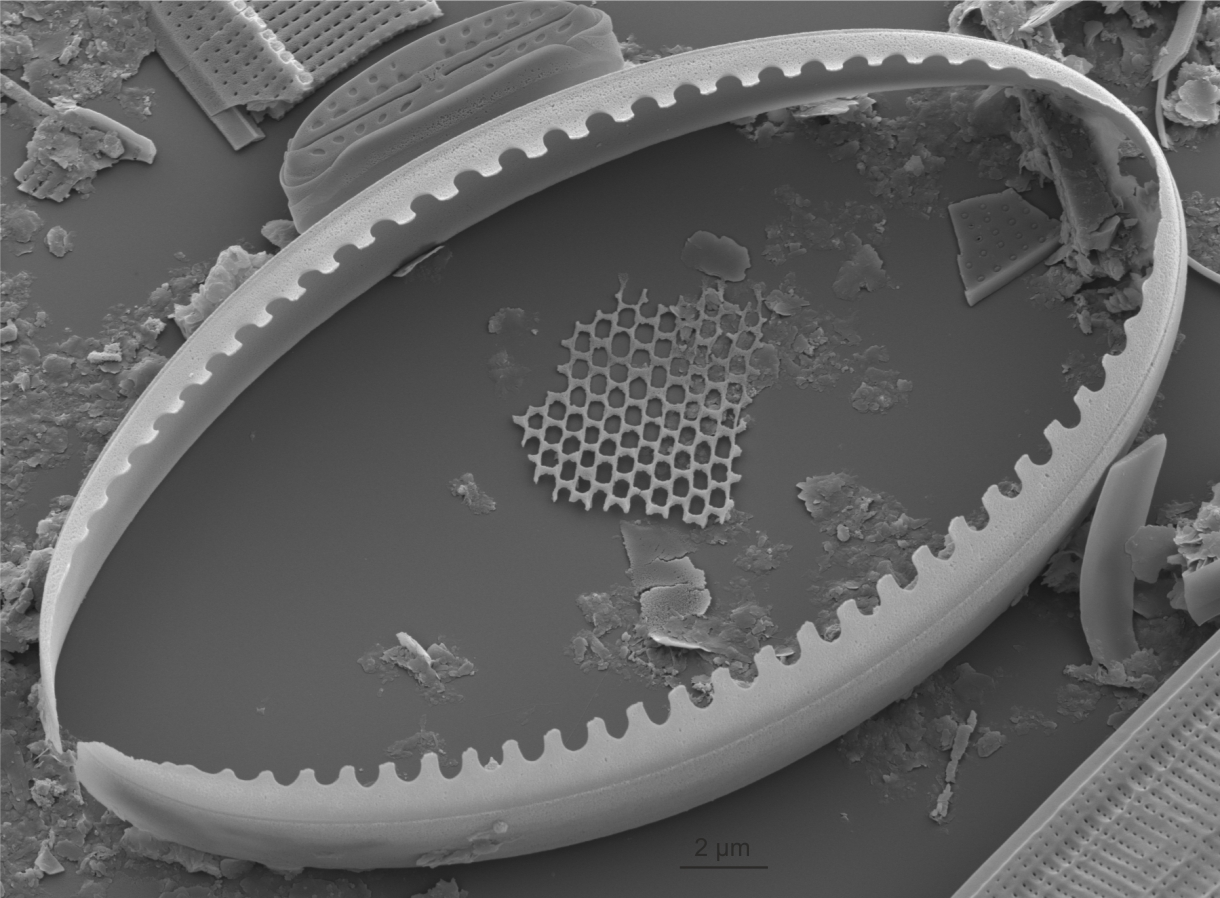 Isolated girdle band of Cocconeis showing undulate margin which overlaps the striae (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
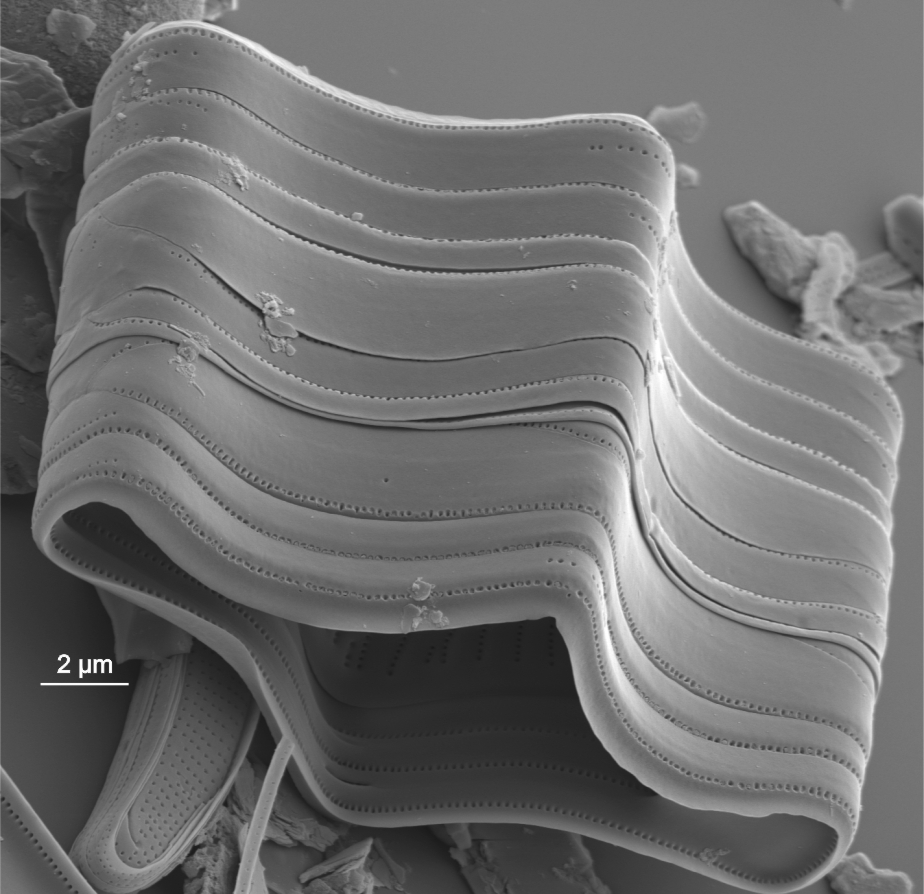 Series of girdle bands of Tabellaria (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Helictoglossa / helictoglossae |
Lipped siliceous thickening terminating the raphe slit internally.
Cox E.J. 1977. Raphe structure in naviculoid diatoms as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft. 54: 261-274.
Notes: Usually seen terminating the raphe slits at valve apices, but may also be present at the central raphe endings in a few taxa. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
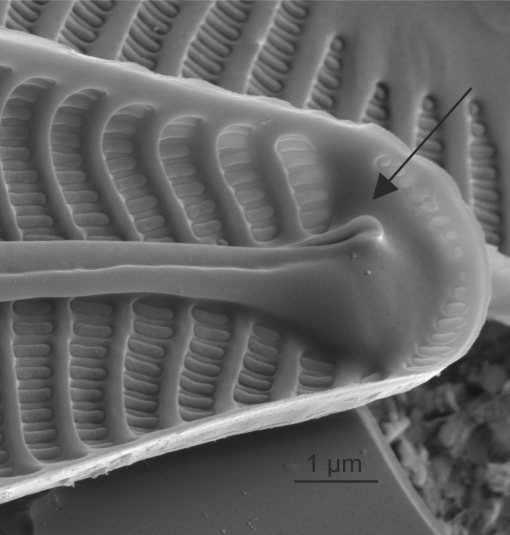 Internal view of helictoglossa in Navicula (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
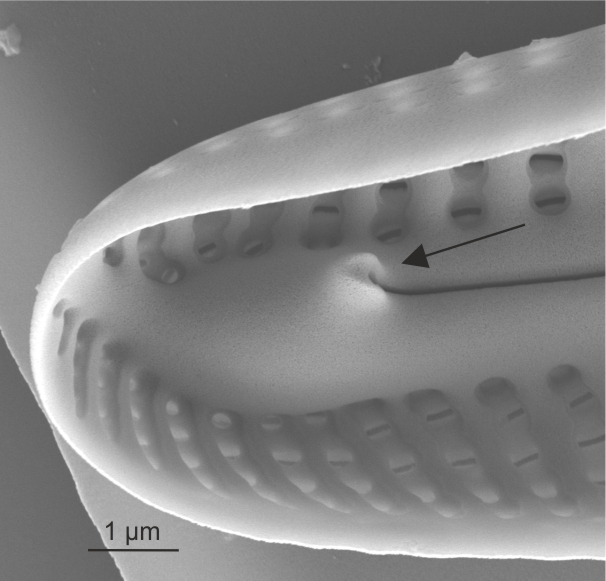 Internal view of helictoglossa in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Horseshoe area |
Area without ornamentation on one side of the valve, defined by a curved internal thickening.
Van de Vijver B., Wetzel C., Kopalova K., Zidarova R,. Ector L. 2013. Analysis of the type material of Achnanthidium lanceolatum Brébisson ex Kützing (Bacillariophyta) with the description of two new Planothidium species from the Antarctic Region. Fottea, Olomouc. 13(2): 105–117.
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
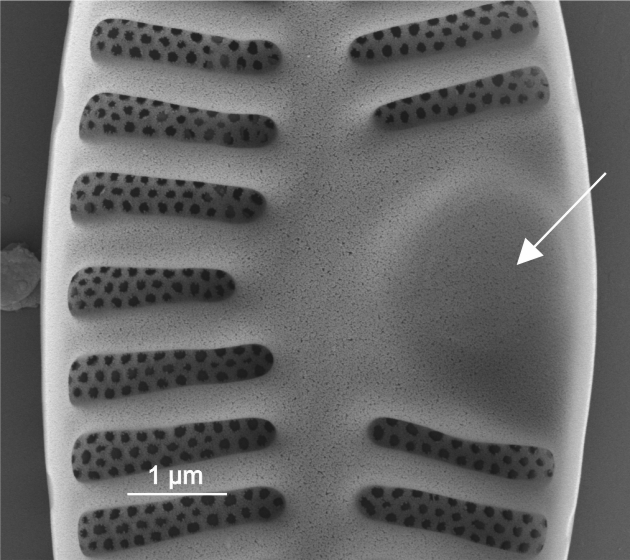 Internal view of horseshoe area in Planothidium (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
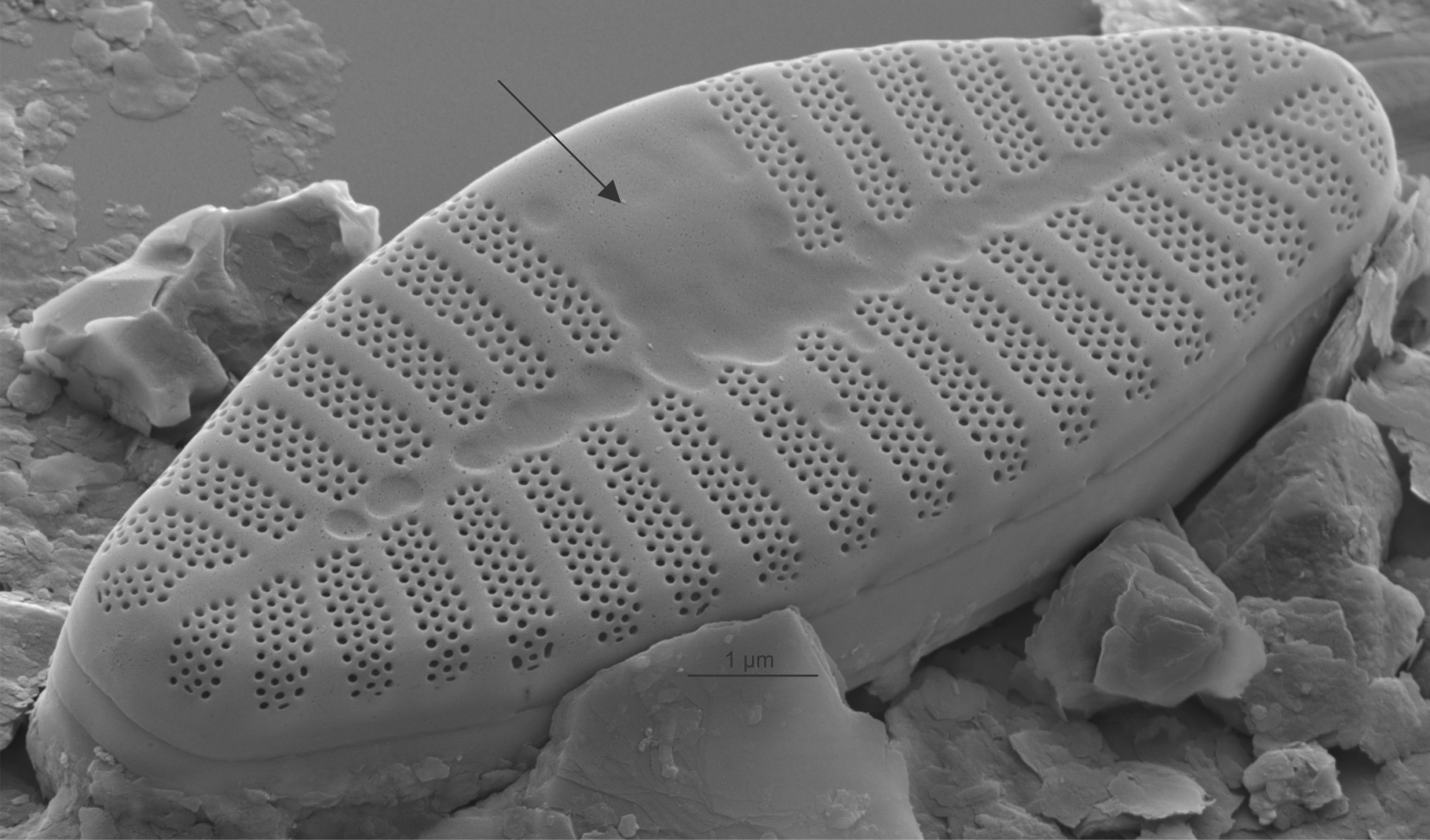 External view of horseshoe area in Planothidium (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
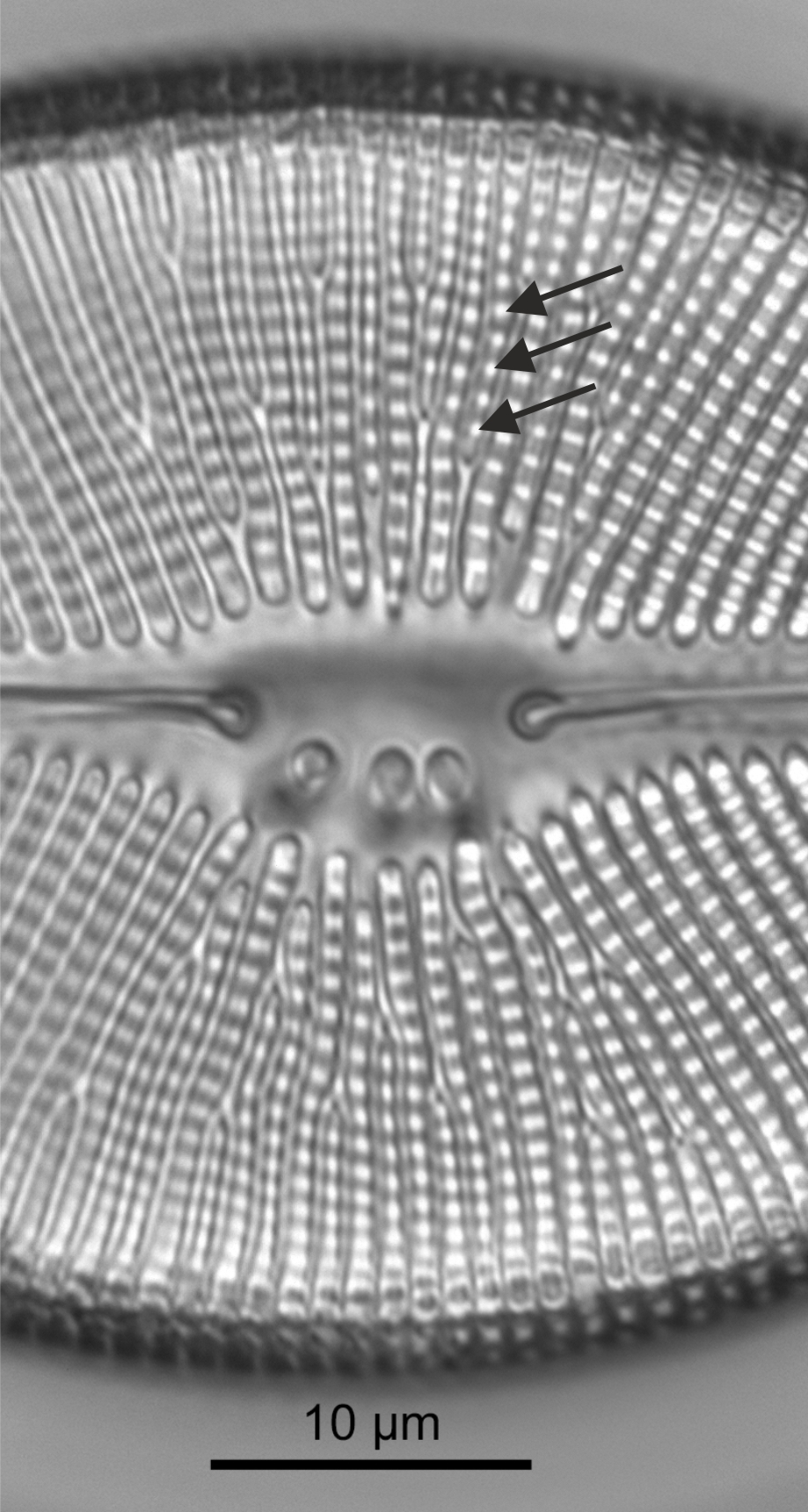
| Isolated pores: stigma / stigmata |
Isolated pores on one (occasionally both) side(s) of the central area with simple external openings; internally with convoluted or dentate surfaces.
Cox E.J. 2012. Ontogeny, homology, and terminology - wall morphogenesis as an aid to character recognition and character state definition for pennate diatom systematics. Journal of Phycology. 48: 1-31.
Notes: Found in genera including Cymbella, Didymosphenia. It is not possible to see the internal structure and distinguish stigmata from stigmoids by LM alone. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
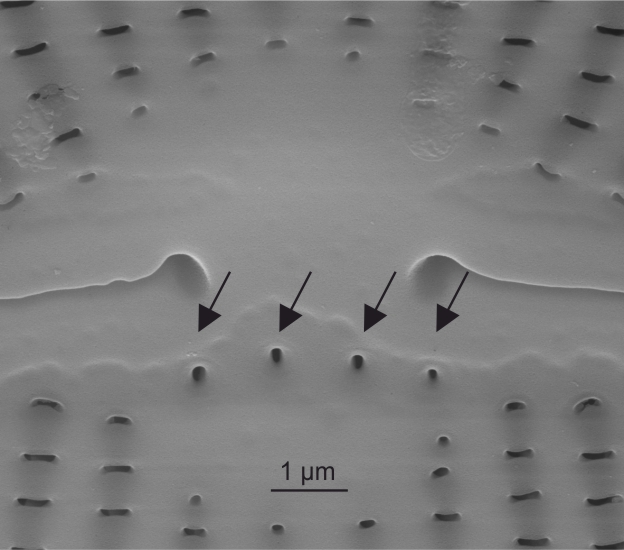 External view of stigmata in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
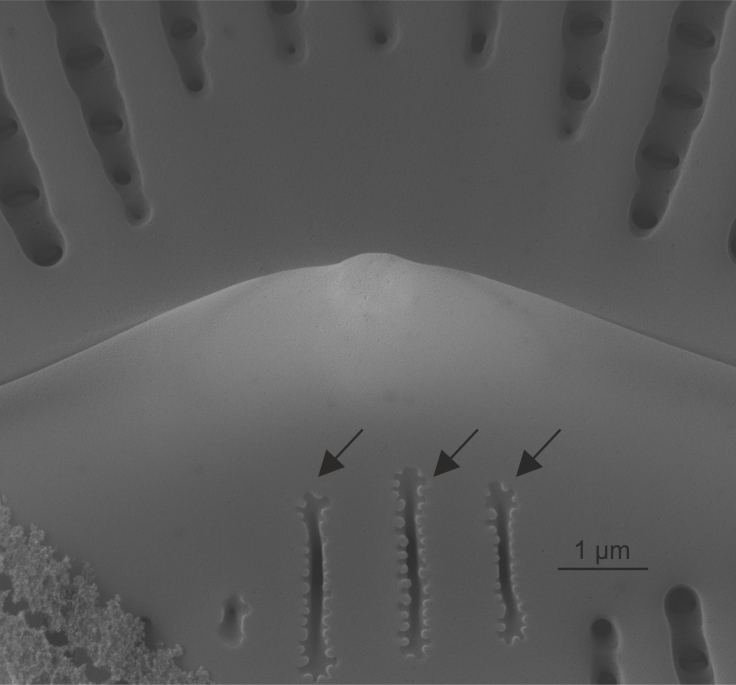 Internal view of stigmata in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
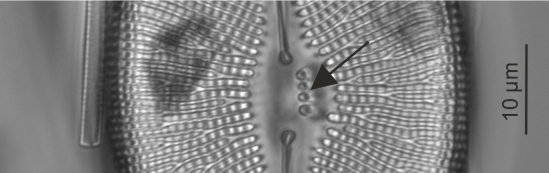 Stigmata in Didymosphenia (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
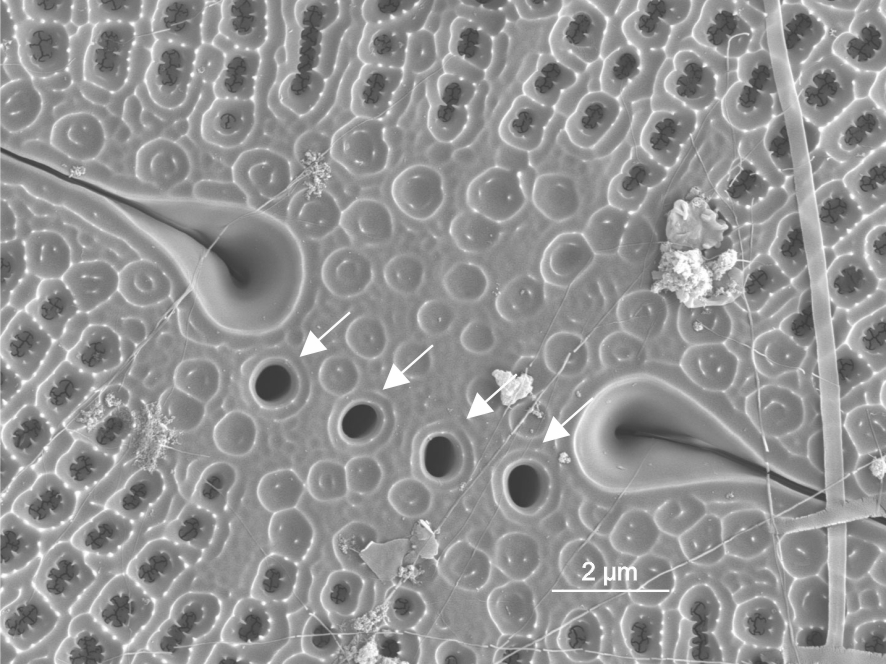 External view of stigmata in Didymosphenia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Internal view of stigmata in Didymosphenia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Isolated pores: stigmoid / stigmoids |
Isolated pores on the primary side of the valve, to one side of the central area, with simple openings to both exterior and interior.
Reichardt E. 1999. Zur Revision der Gattung Gomphonema. Die Arten um G. affine/insigne, G. angustatum/micropus, G. acuminatum sowie gomphonemoide Diatomeen aus dem Oberoligozän in Böhmen. Iconographia Diatomologica, Vol. 8, Koeltz Scientific Books, A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, Ruggell. 203 pp
Levkov Z., Mitic-Kopanja D., Reichardt E. 2016. The diatom genus Gomphonema from the Republic of Macedonia. Lange-Bertalot H. (ed.) Diatoms of Europe, Vol. 8, Koeltz Botanical Books, Oberreifenberg. 552 pp
Krammer K. 1997. Die cymbelloiden Diatomeen. Eine Monographie der weltweit bekannten Taxa. Teil 2. Encyonema part., Encyonopsis and Cymbellopsis. Bibliotheca Diatomologica, Vol. 37, J. Cramer, Berlin. 469 pp
Notes: Found in Gomphonema, Encyonema, Encyonopsis, Gomphocymbella. It is not possible to distinguish stigmoids from stigmata by LM alone. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 External view of stigmoid in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Internal view of stigmoid in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Porte-crayon endings |
Fused helictoglossa and axial ribs forming the shape of the tip of a propelling pencil.
Cox E.J. 1975. A reappraisal of the diatom genus Amphipleura Kütz. using light and electron microscopy. British Phycological Journal. 10(1): 1-12.
Notes: Characteristic of Frustulia, Amphipleura. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Porte-crayon ending in Frustulia (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
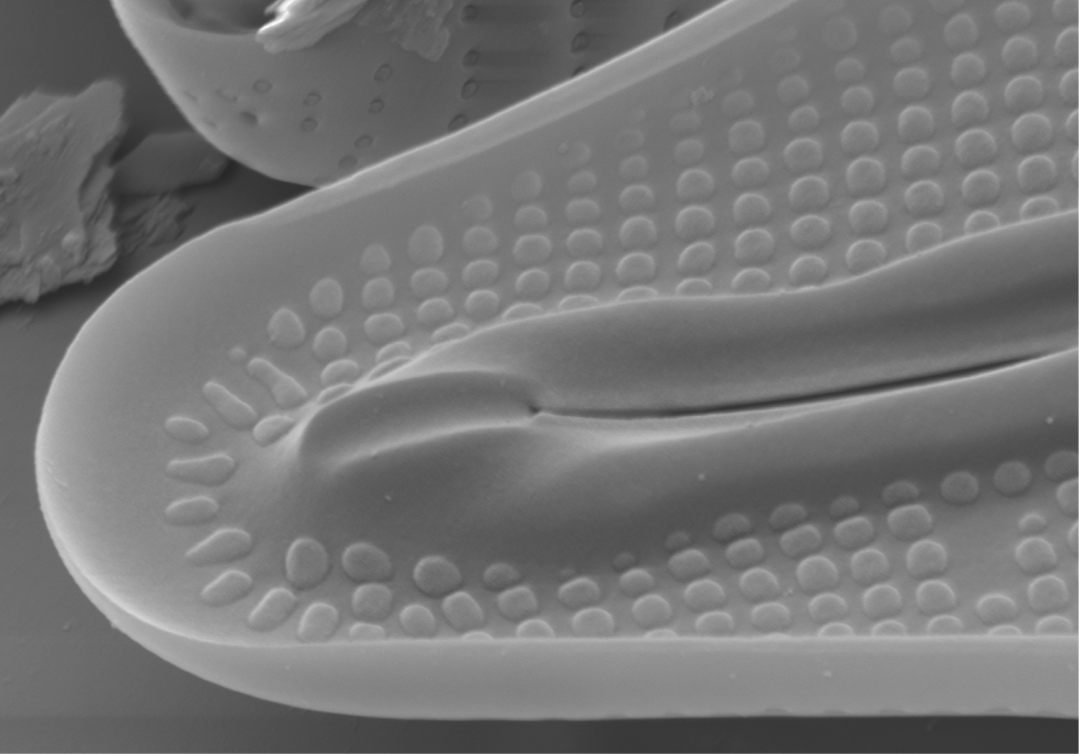 Internal view of porte-crayon in Frustulia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Primary side of valve |
First formed side of a raphid valve; the side away from the Voigt discontinuity
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
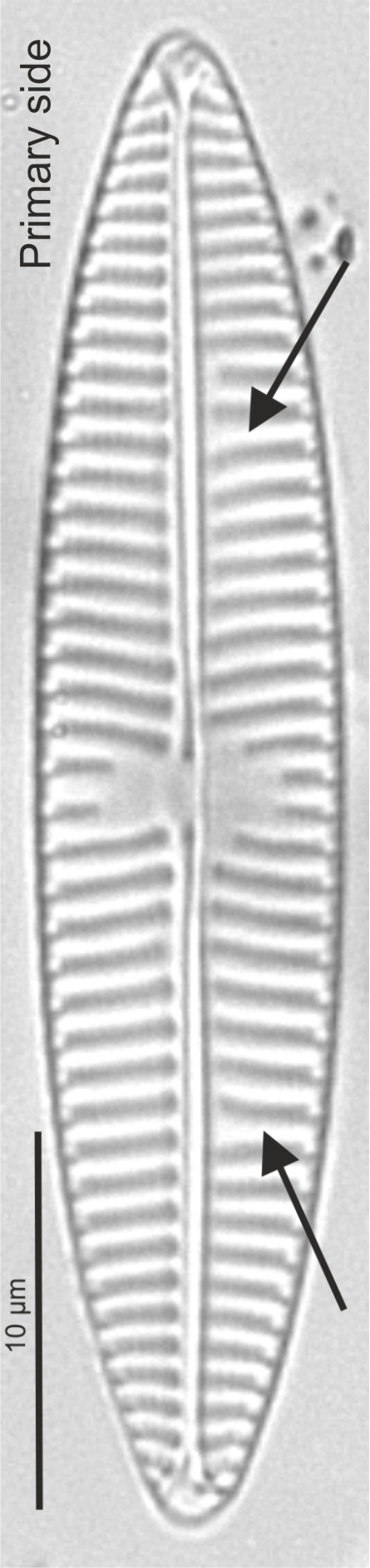 Primary side and Voigt discontinuity in Navicula (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
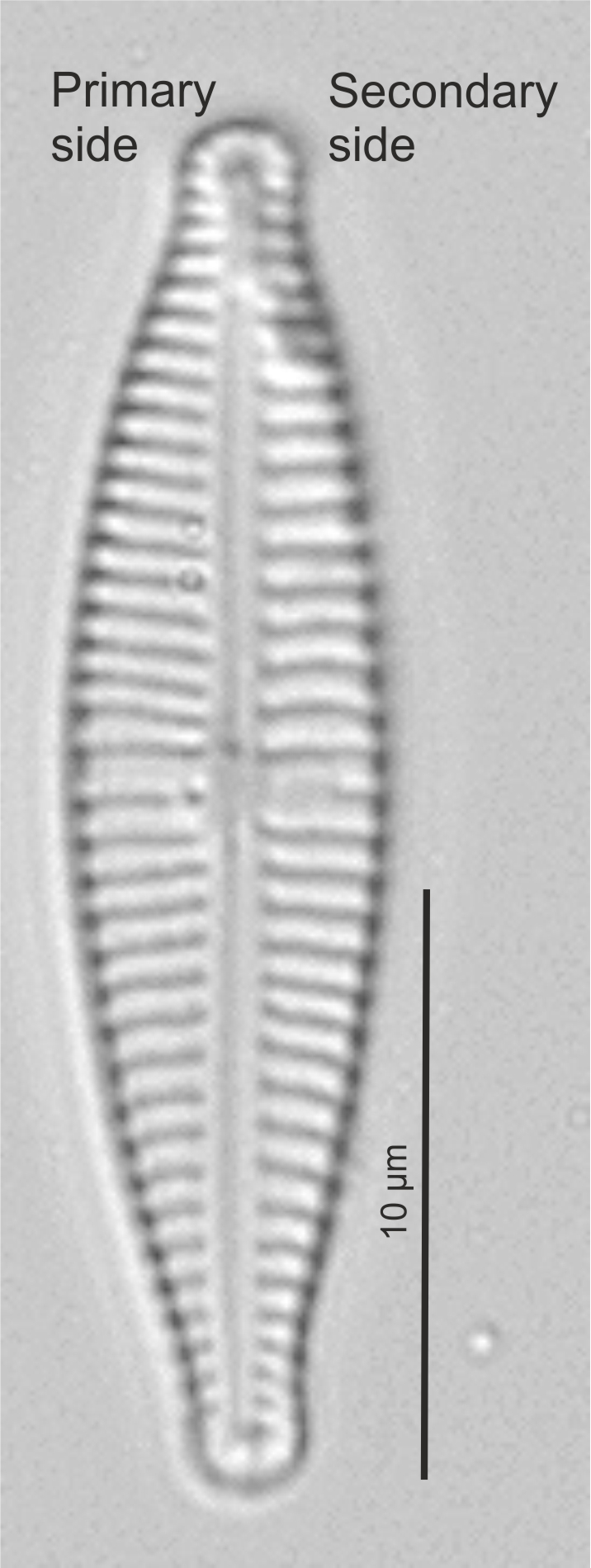 Primary and secondary side in Gomphonena (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
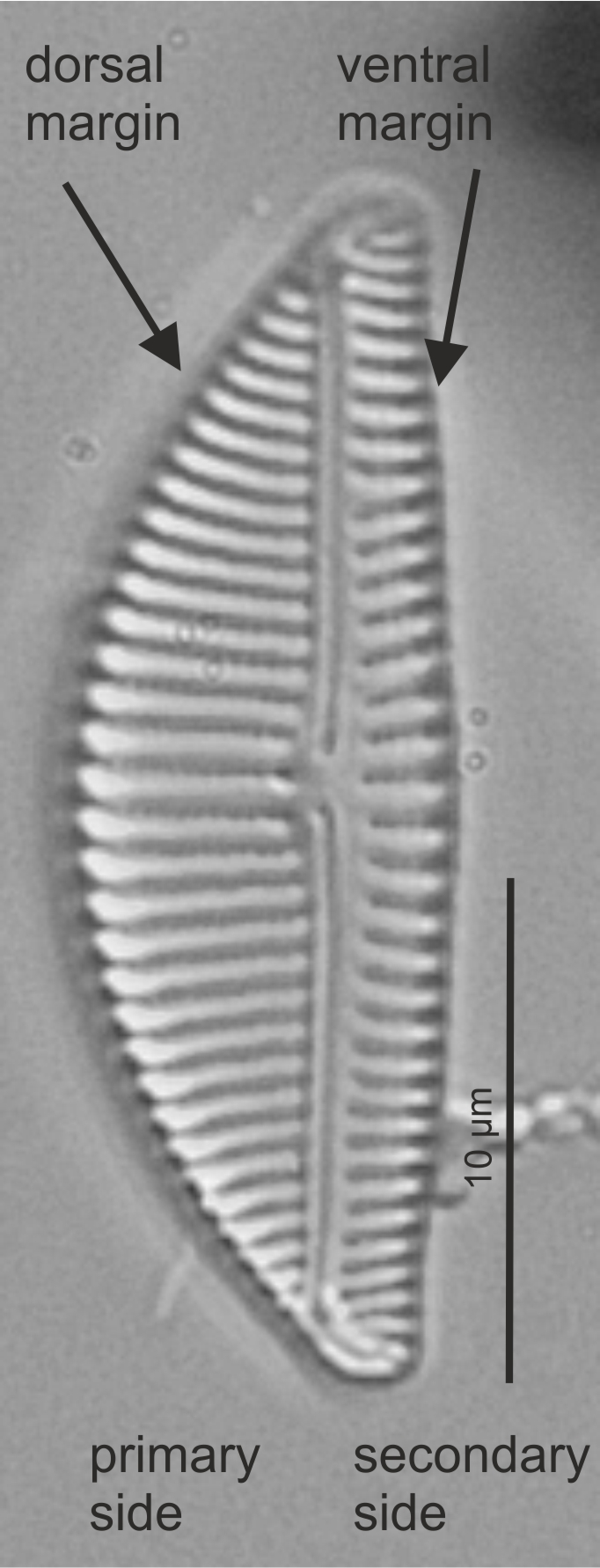 Primary and secondary side in Encyonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
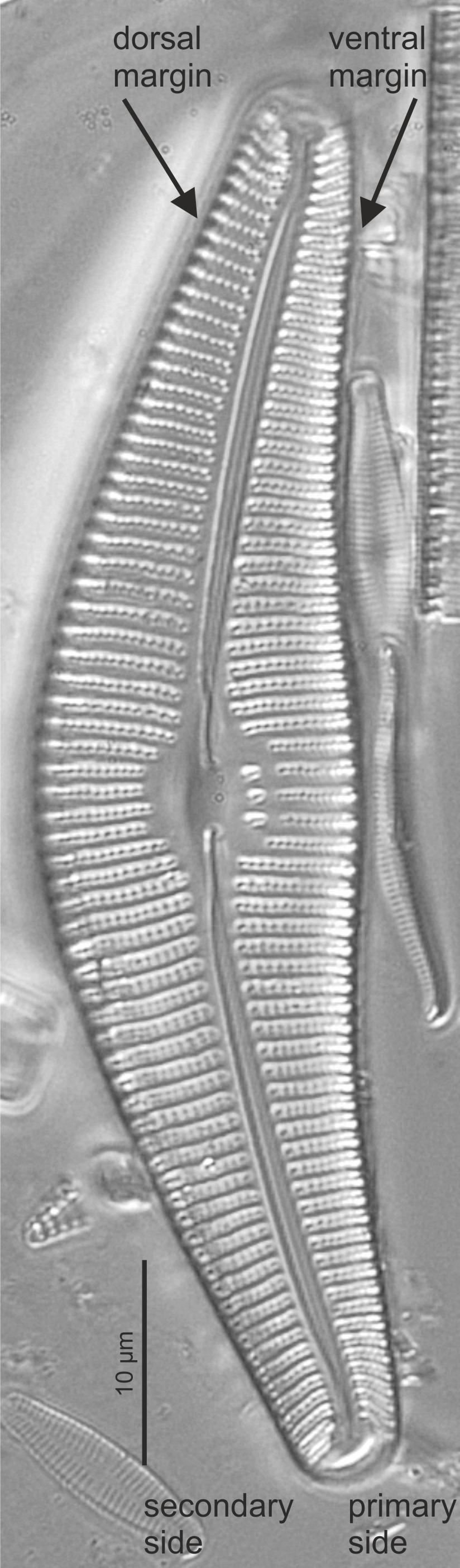 Primary and secondary side in Cymbella (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Pseudoseptum / pseudosepta |
A thin plate of silica at the apex of a pennate diatom.
Kociolek J. P., Spaulding S. A., Sabbe K., Vyverman W. 2004. New Gomphonema (Bacillariophyta) species from Tasmania. Phycologia. 43: 427-444.
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
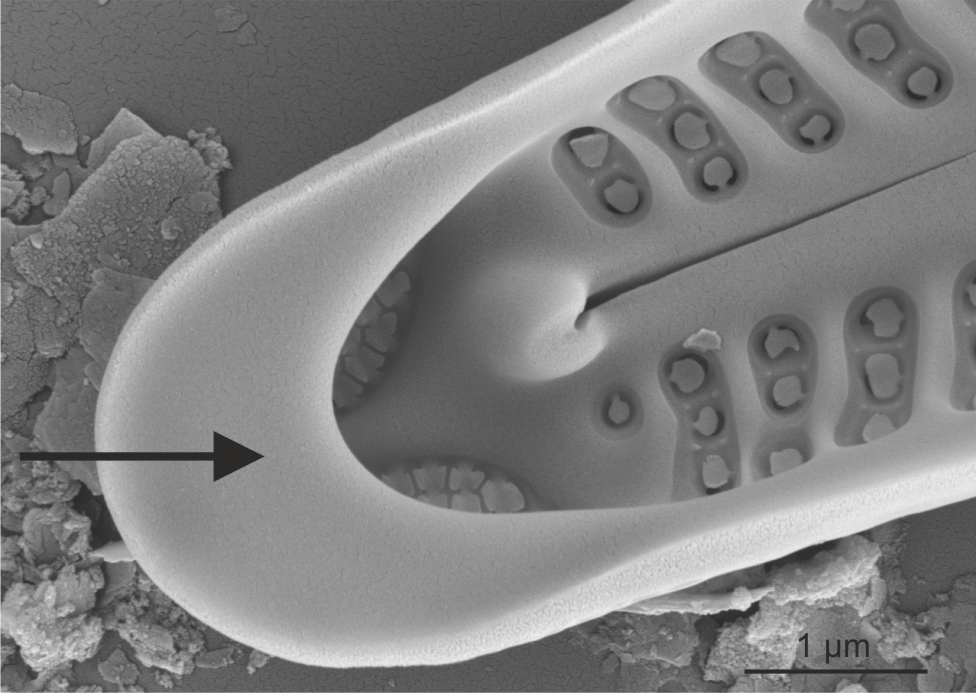 Pseudoseptum in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Raphe |
Paired slits through the valve along the long axis of pennate diatoms, around the valve margins in surirelloid diatoms, associated with motility.
Barber H.G., Haworth E.Y. 1981. A Guide to the Morphology of the Diatom Frustule. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside. 112 pp
Cox E.J. 2012. Ontogeny, homology, and terminology - wall morphogenesis as an aid to character recognition and character state definition for pennate diatom systematics. Journal of Phycology. 48: 1-31.
Ross R., Cox E.J., Karayeva N.I., Mann D.G., Paddock T.B.B., Simonsen R., Sims P.A. 1979. An Amended Terminology for the Siliceous Components of the Diatom Cell. Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft. 64: 513-533.
Notes: The raphe slits are subtended by struts (fibulae) in nitzschioid and surirelloid diatoms. See fibula. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Raphe in Navicula (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Raphe in Cavinula (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Raphe in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
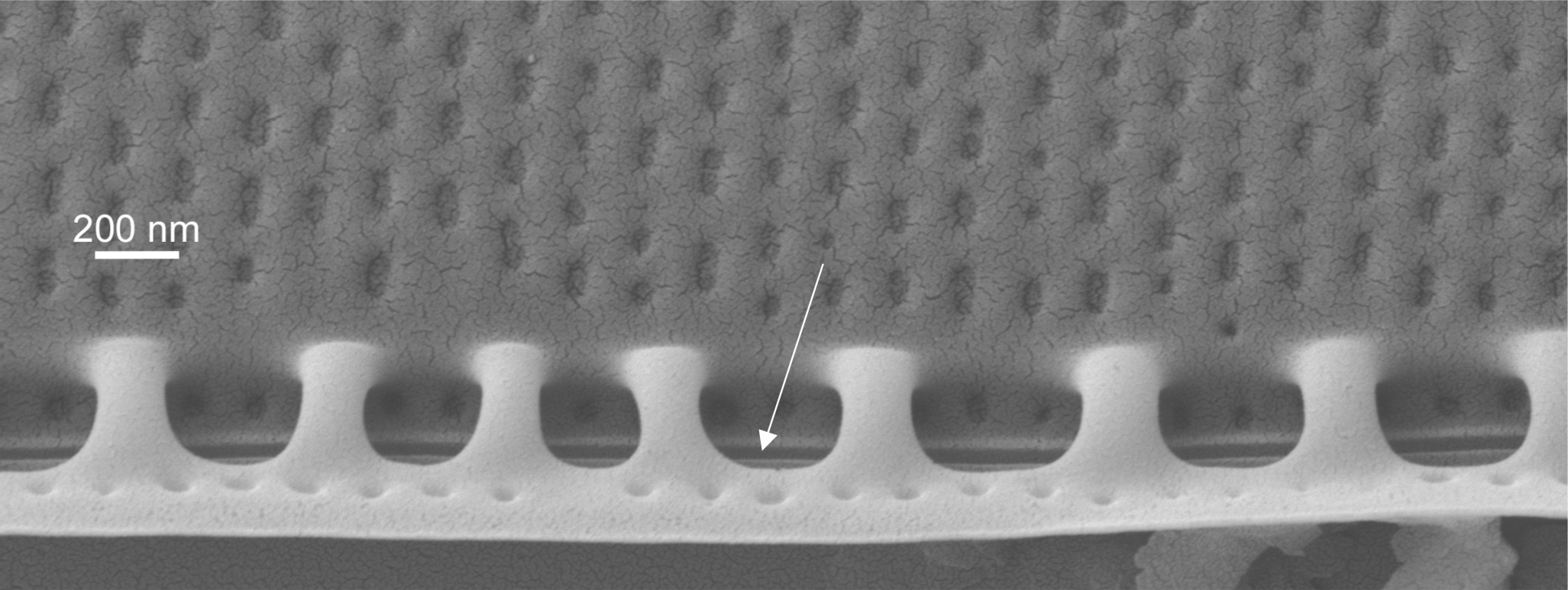 Raphe in Nitzschia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
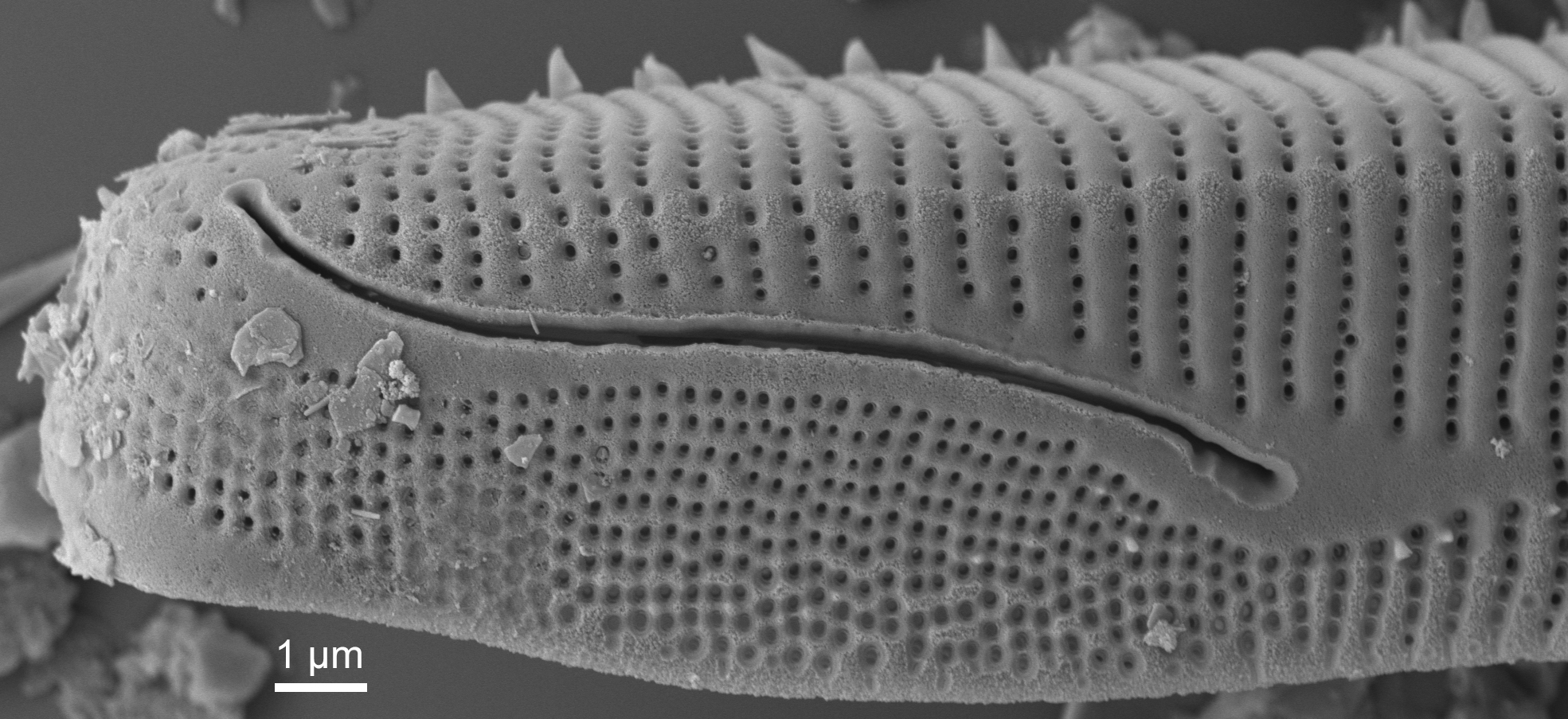 Raphe in Eunotia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Rimoportula / rimoportulae |
A process in the valve with a simple external pore, internally lipped. Formerly known as a labiate process.
Cox E.J., Kennaway G M. 2002. Studies of valve morphogenesis in pennate diatoms: investigating aspects of cell biology in a systematic context. Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Diatom Symposium, Poulin M. (ed.), Biopress, Bristol. 35-48 pp
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Notes: Found in centric, araphid and eunotioid diatoms. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
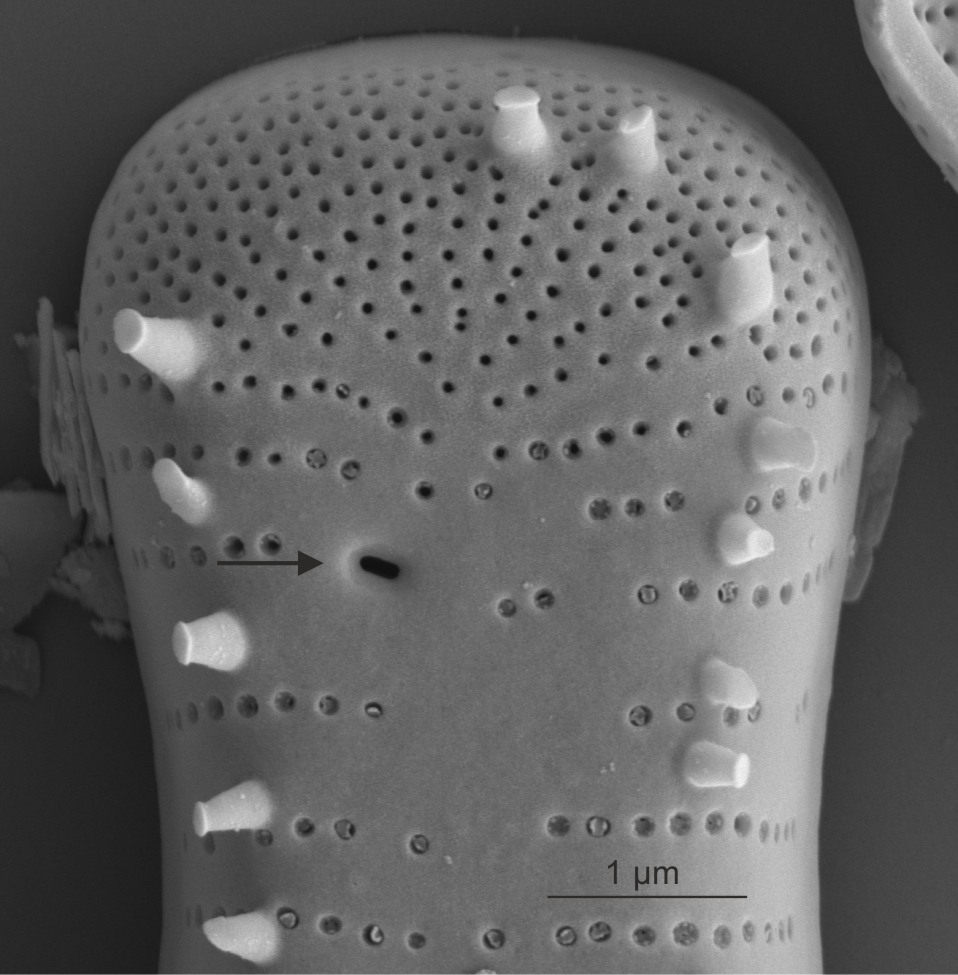 External view of rimoportula in Tabellaria (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
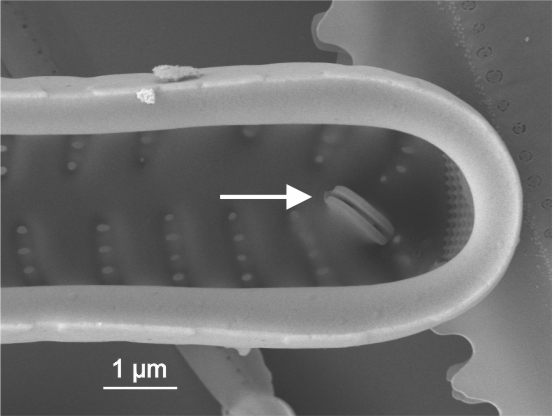 Internal view of rimoportula in Ulnaria (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Secondary side of valve |
Side of valve in a raphid diatom with the Voigt discontinuity.
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
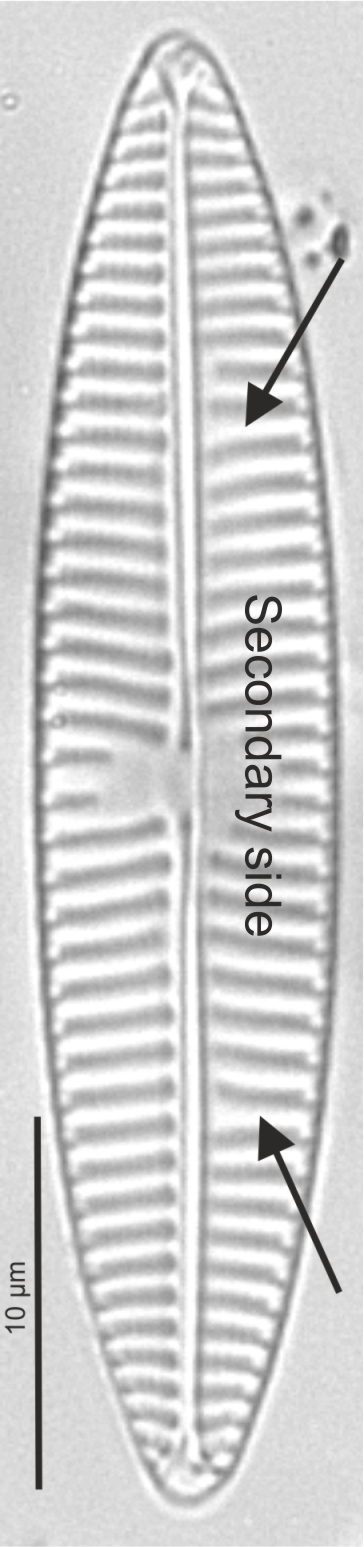 Secondary side and voigt discontinuity in Navicula (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Septum / septa |
A thin plate of silica bridging the sides of a girdle band, particularly characteristic of some araphid genera.
Sato S., Mann D.G., Matsumoto S., Medlin L.K. 2008. Pseudostriatella (Bacillariophyta): a description of a new araphid diatom genus based on observations of frustule and auxospore structure and 18S rDNA phylogeny. Phycologia. 47(4): 371-391.
Lange-Bertalot H. 1988. Die Gattung Tabellaria unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Tabellaria ventricosa Kützing (Bacillariophyceae). Nova Hedwigia. 46(3-4): 413-431.
Notes: The septum extends from the solid longitudinal rib of the girdle band, probably starting to grow from the central portion of the band. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
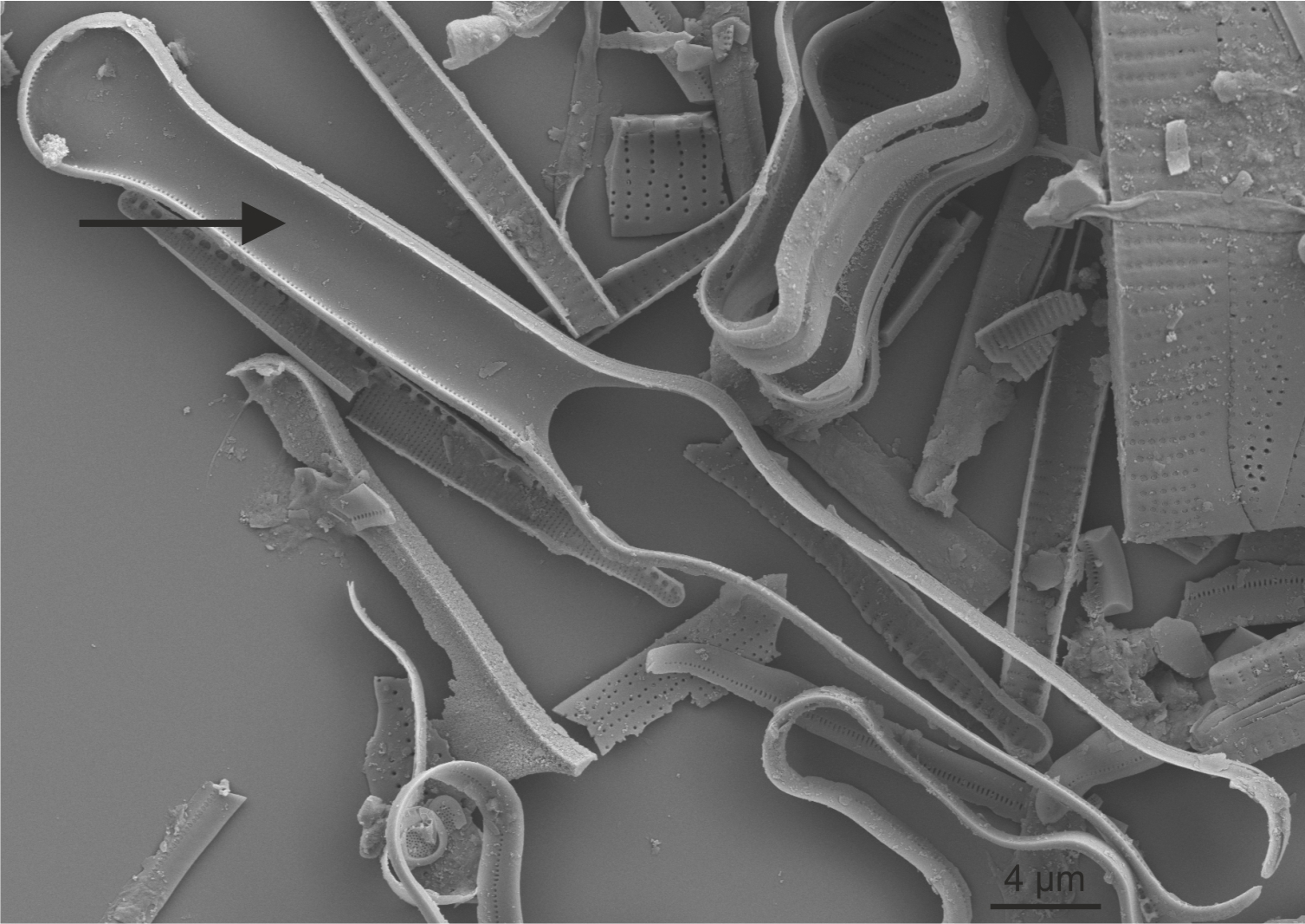 Septum in Tabellaria (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
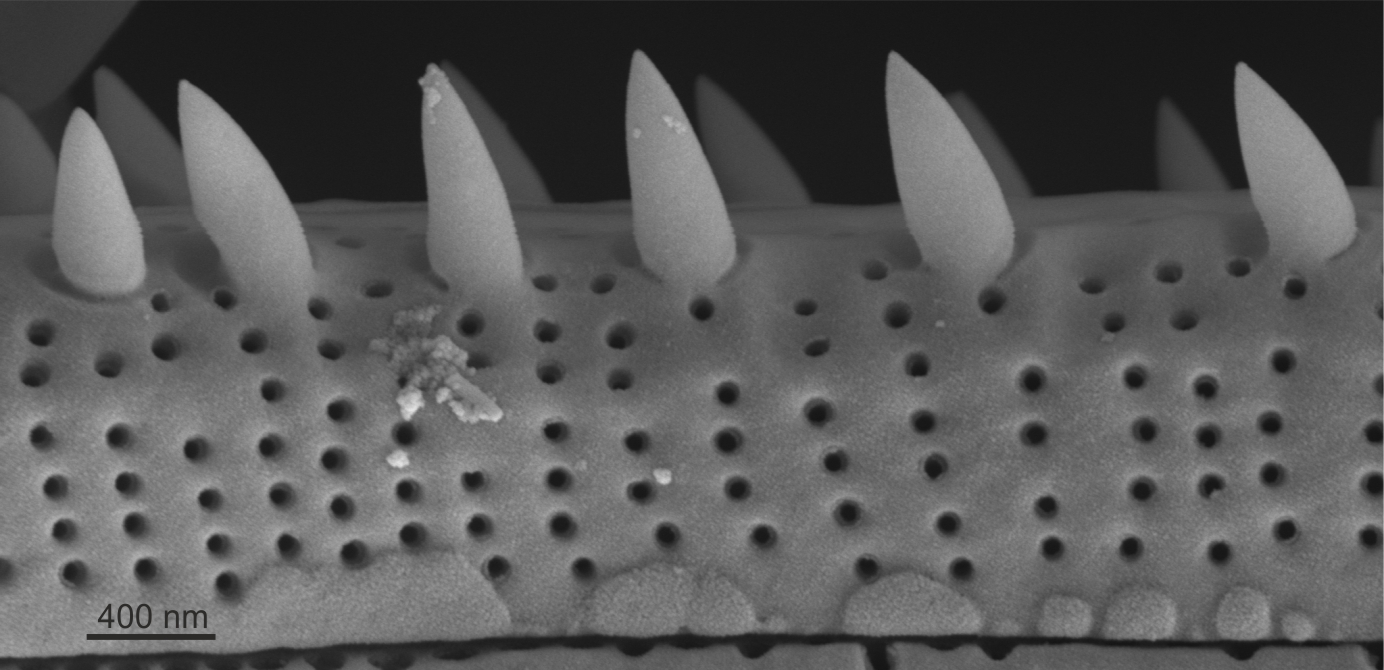
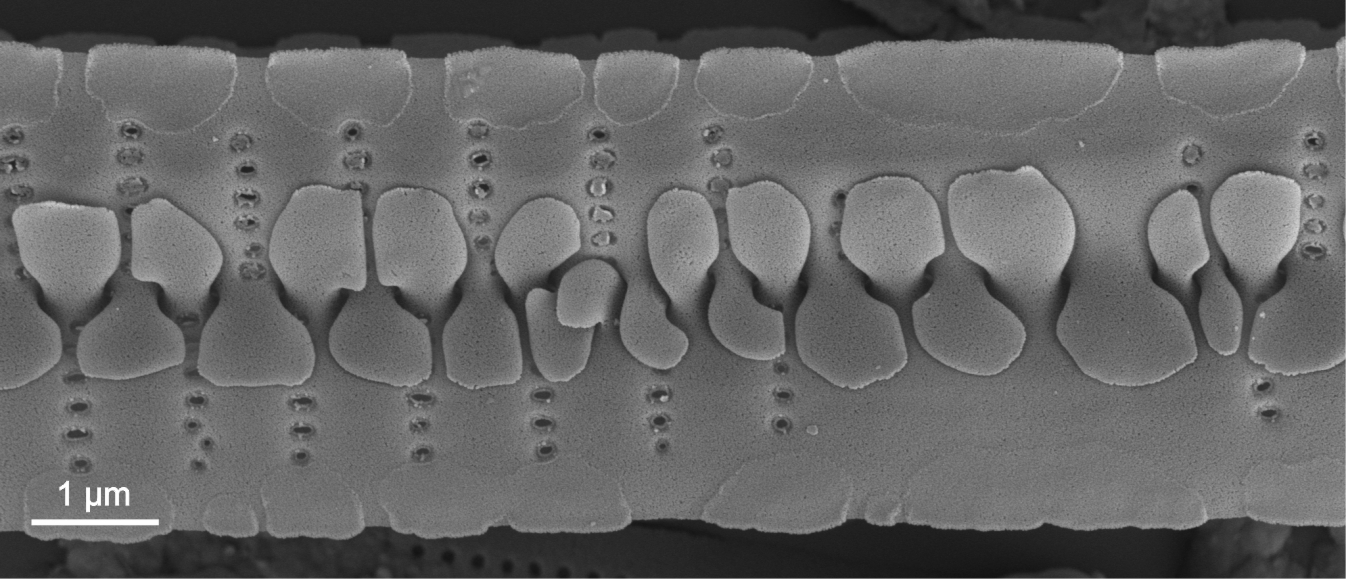
| Spines, granules |
Spiky or globular surface siliceous structures on the outer surface of diatom valves.
Morales E.A. 2001. Morphological studies in selected fragilarioid diatoms (Bacillariophyceae) from Connecticut waters (U.S.A.). Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 151: 105-120.
Notes: Spines are often found at the valve face/mantle junction, on or between virgae, or irregularly spaced. They may also perform a linking function between sibling valves enabling the development of colonies.
Granules are usually randomly spaced. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
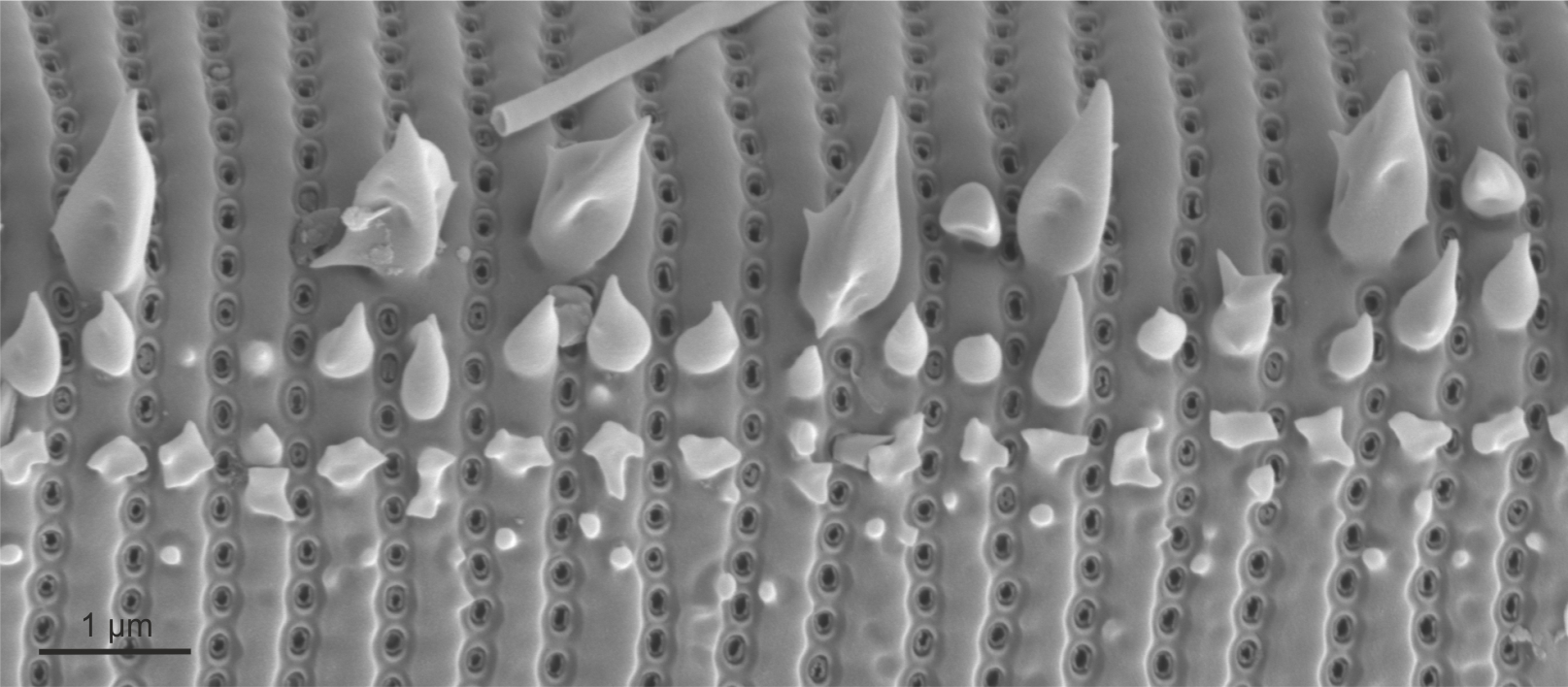 Spines in Eunotia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Spines in Peronia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Spines in Peronia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Interlinking spines in Fragilaria (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Sternum |
Area without ornamentation along the long axis of the valve, usually along the centre of the valve in araphid or monoraphid diatoms (previously referred to as pseudoraphe in monoraphids).
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
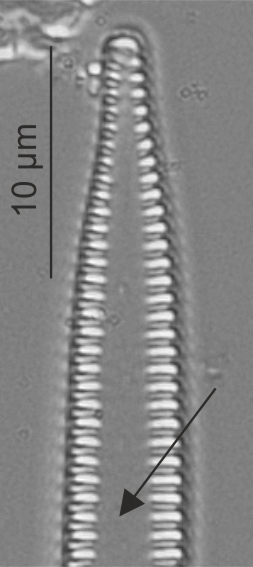 Sternum in Tabularia (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Sternum in Cocconeis (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Stria / striae |
Lines on the valve formed by rows of areolae.
Ross R., Cox E.J., Karayeva N.I., Mann D.G., Paddock T.B.B., Simonsen R., Sims P.A. 1979. An Amended Terminology for the Siliceous Components of the Diatom Cell. Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft. 64: 513-533.
Cox E.J. 2011. Morphology, cell wall, cytology, ultrastructure, and morphogenetic studies. Overview and specific observations. The Diatom World, Cellular origin, life in extreme habitats and astrobiology, Seckbach J., Kociolek J.P. (eds), 19. 21-45 pp
Cox E.J. 2012. Ontogeny, homology, and terminology - wall morphogenesis as an aid to character recognition and character state definition for pennate diatom systematics. Journal of Phycology. 48: 1-31.
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Barber H.G., Haworth E.Y. 1981. A Guide to the Morphology of the Diatom Frustule. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside. 112 pp
Cox E.J. 1999. Variation in patterns of valve morphogenesis between representatives of six biraphid diatom genera (Bacillariophyceae). Journal of Phycology. 35: 1297-1312.
Notes: Orientation and density are important species specific characters. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
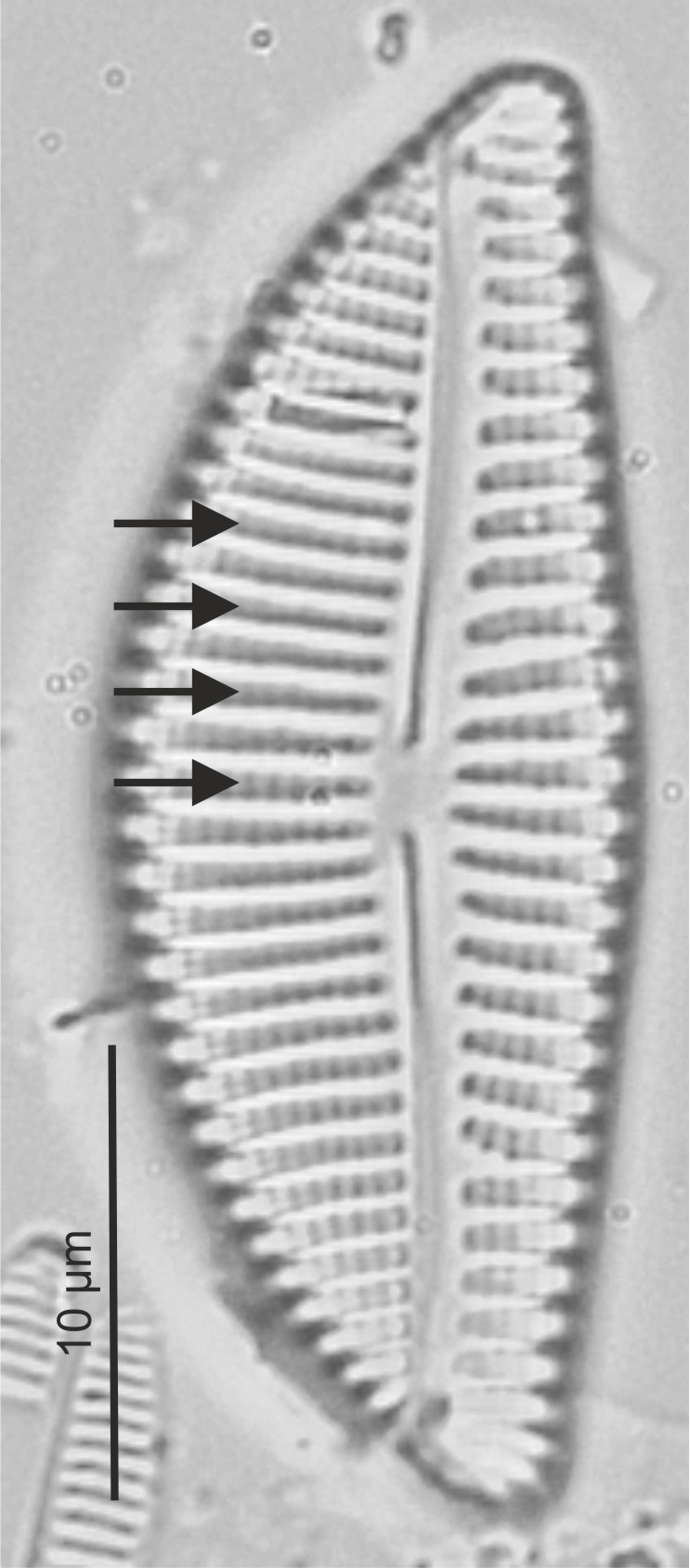 Striae in Encyonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Striae in Encyonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Alveolate striae in Pinnularia (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
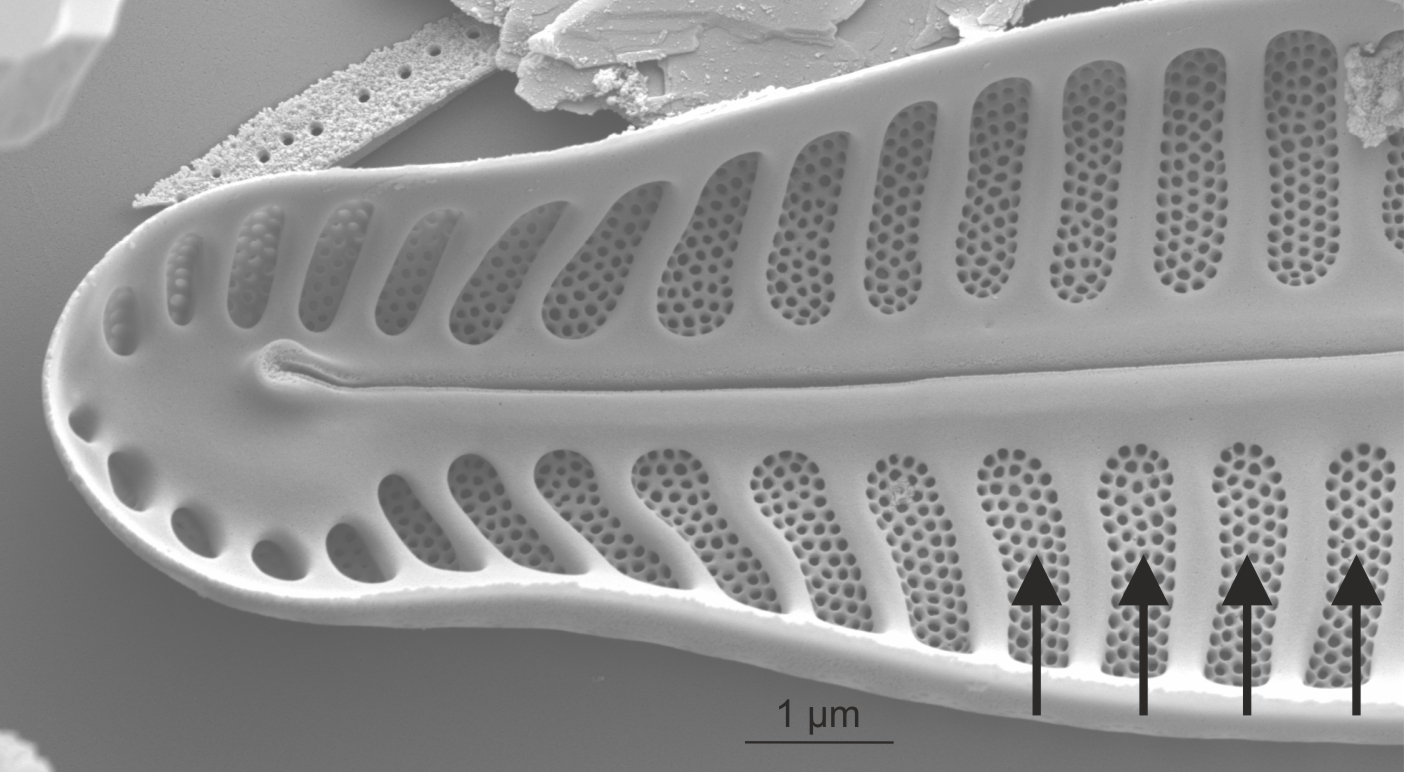 Alveolate striae in Pinnularia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Striae: Voigt discontinuity |
The point on one side of the raphe sternum where the forming ribs met, often identifiable by a slight irregularity in the striae. There are two discontinuities per raphe system, one alongside each slit, at the same distance from the apices in each case.
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Notes: The Voigt discontinuity identifies the secondary side of a raphid valve. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Voigt discontinuity in Navicula (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Valve symmetry: dorsiventral |
One long side of a pennate valve more curved than the other, or one side convex the other concave.
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Notes: Either the primary or the secondary side of the valve can be more curved than the other. This discriminates between cymbelloid genera. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Dorsiventral valve in Encyonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
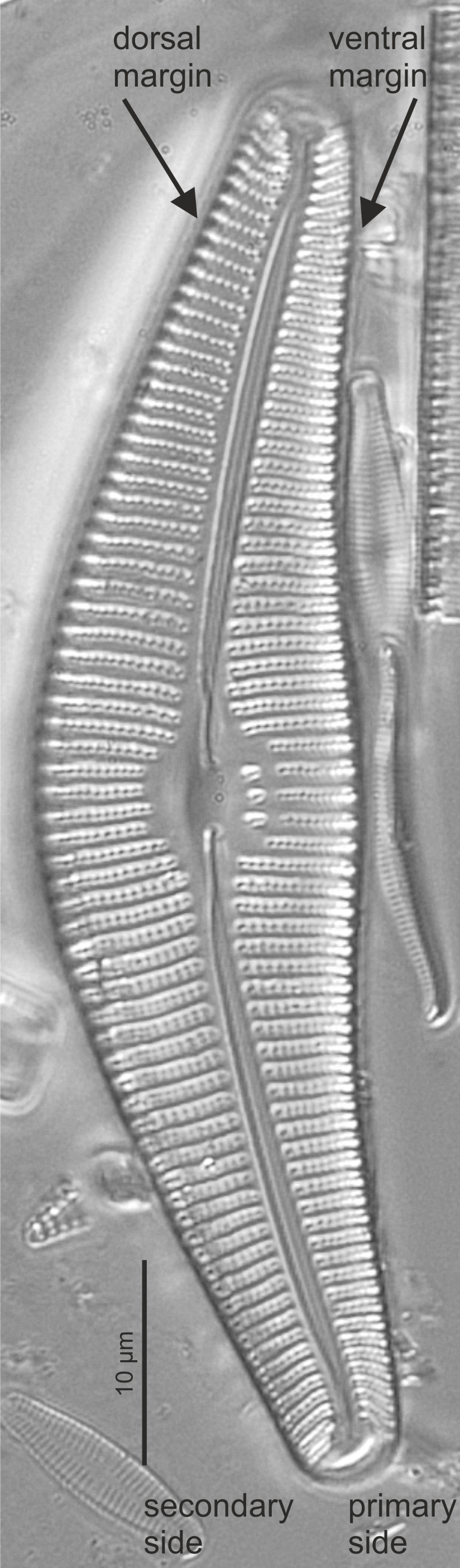 Dorsiventral valve in Cymbella (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Valve: foot pole |
The narrower pole of a heteropolar diatom, usually a point of attachment to a surface.
Levkov Z., Mitic-Kopanja D., Reichardt E. 2016. The diatom genus Gomphonema from the Republic of Macedonia. Lange-Bertalot H. (ed.) Diatoms of Europe, Vol. 8, Koeltz Botanical Books, Oberreifenberg. 552 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
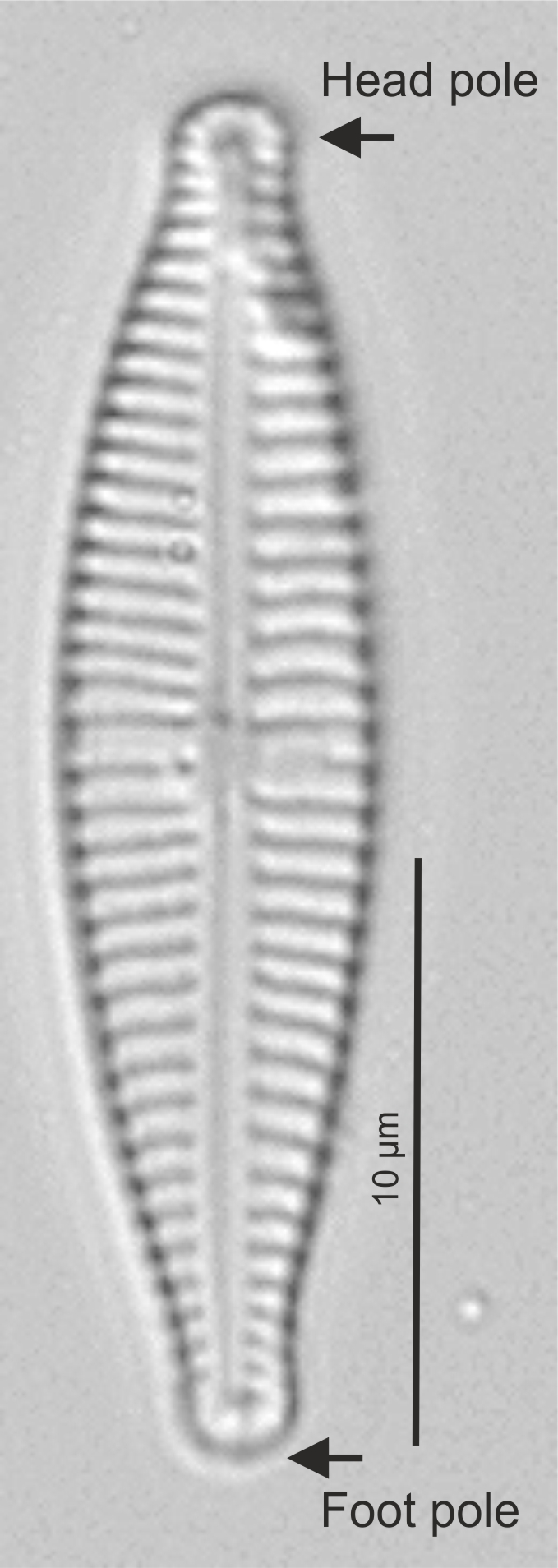 Head and foot pole in Gomphonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Valve: head pole |
The broader pole of a heteropolar diatom.
Levlov Z., Mitić-Kopanja D., Reichardt E. 2016. The diatom genus Gomphonema from the Republic of Macedonia. 8. Diatoms of Europe. 552 pp
Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
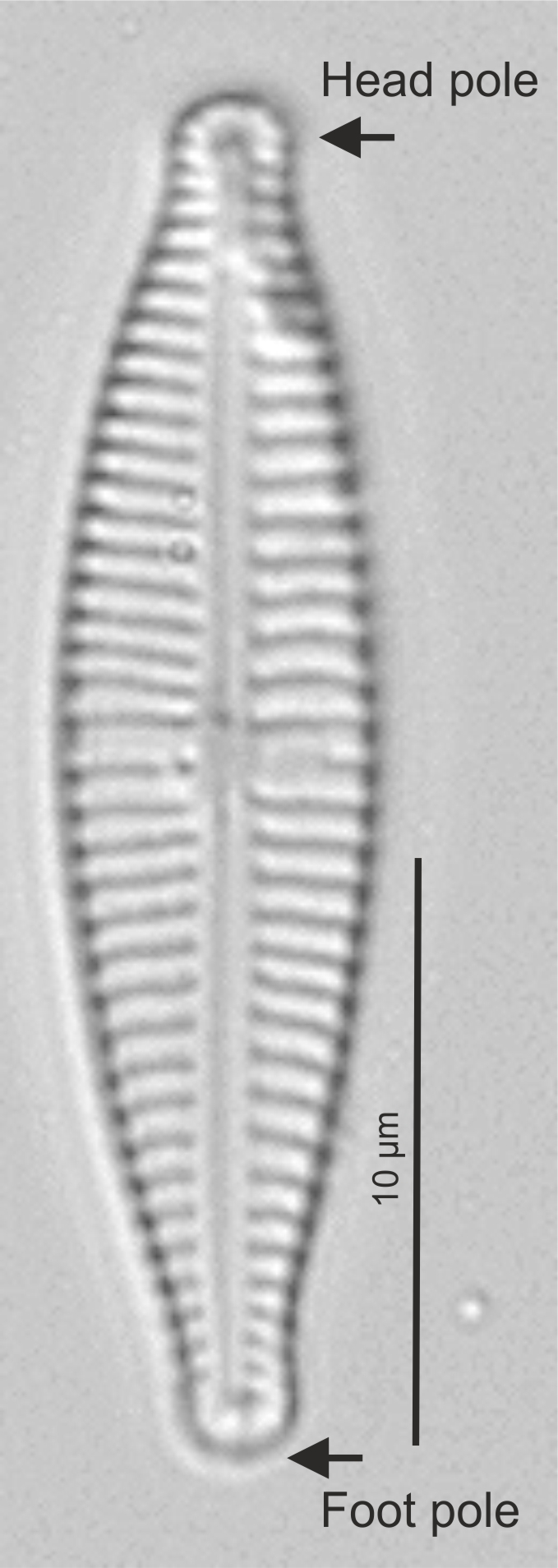 Head and foot pole in Gomphonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Valve: mantle |
The edge of a valve that is visible in girdle view adjoining the cingulum.
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Notes: The distinction between face and mantle is very clear in some taxa, far less so in others. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
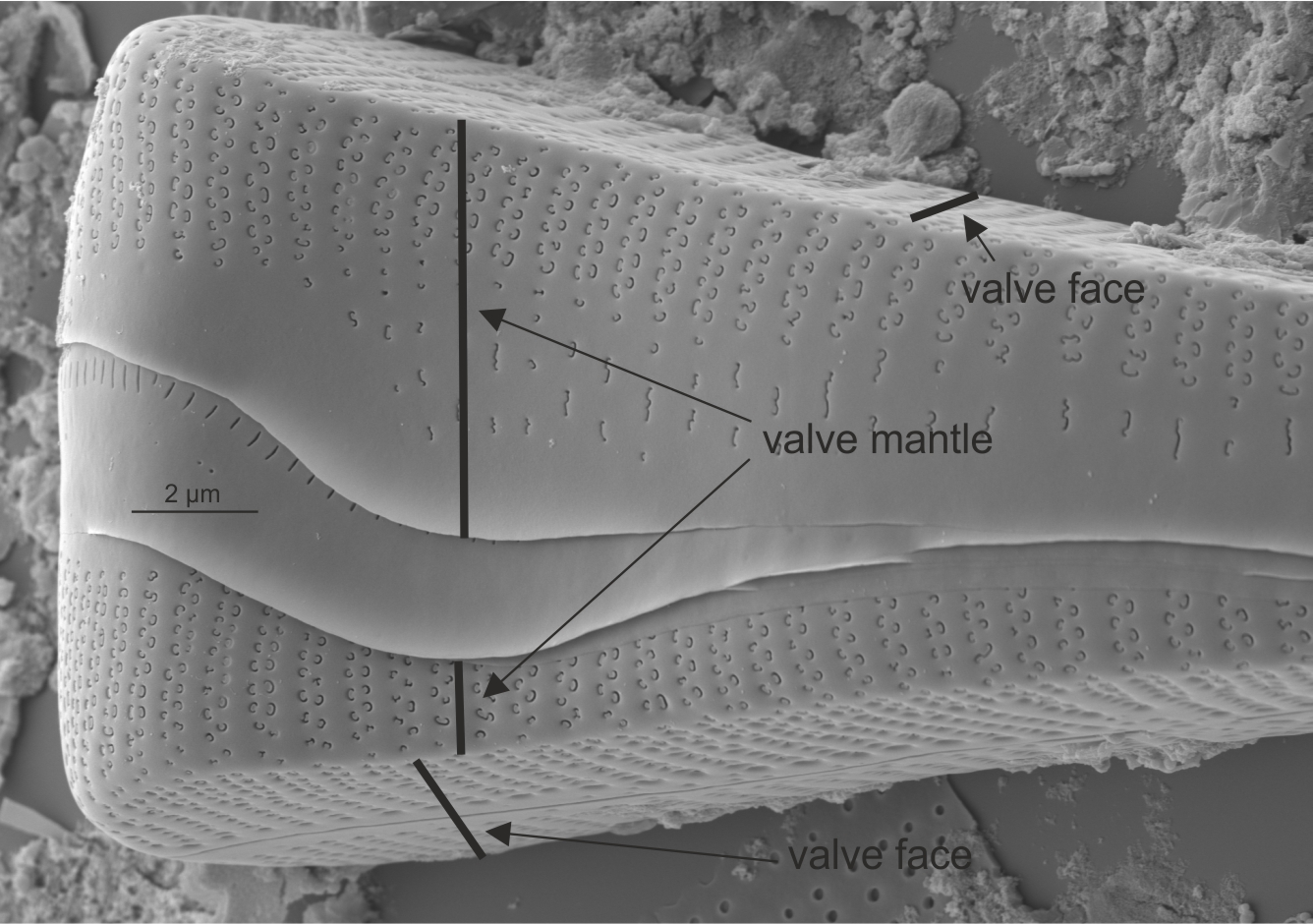 Mantle in Gomphonema (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
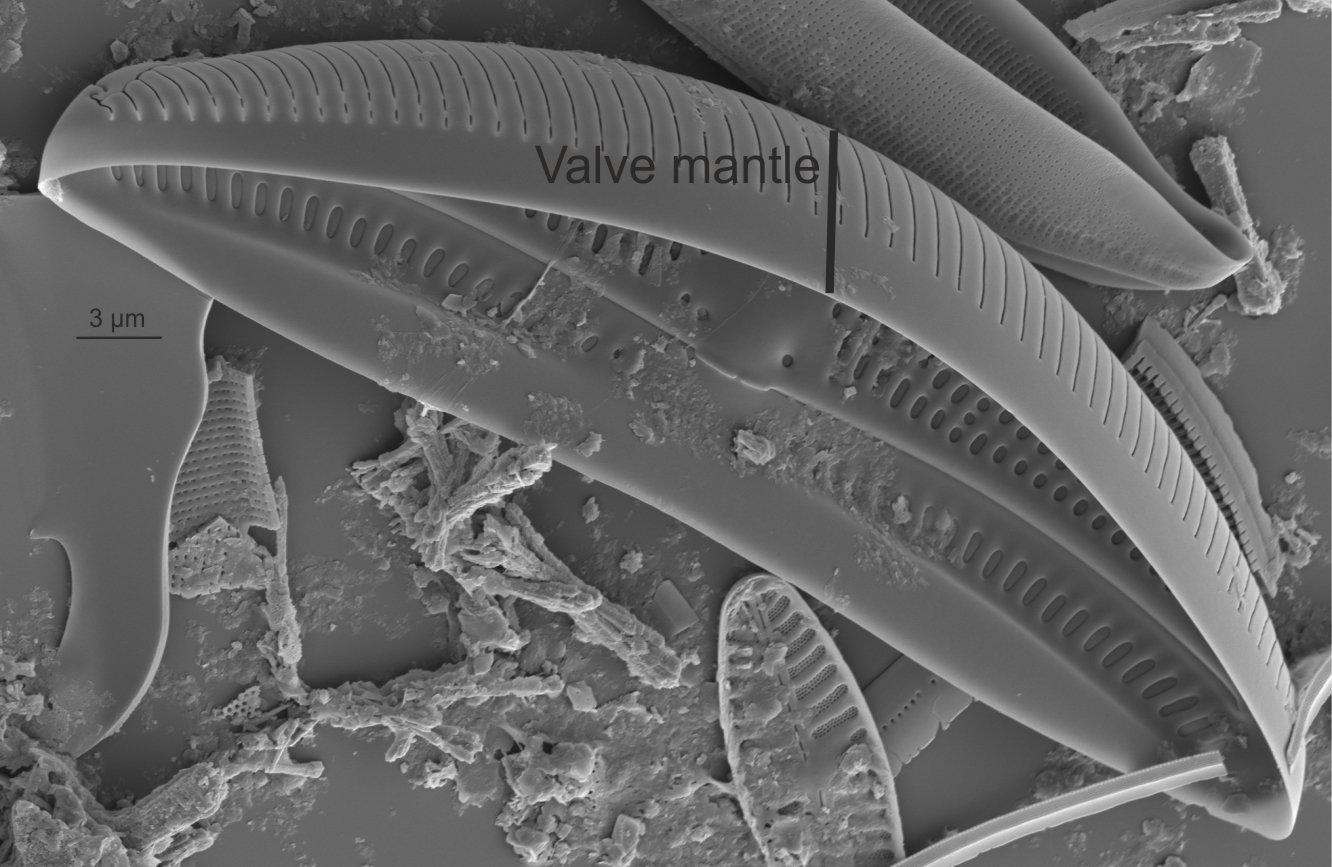 Mantle in Amphora (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
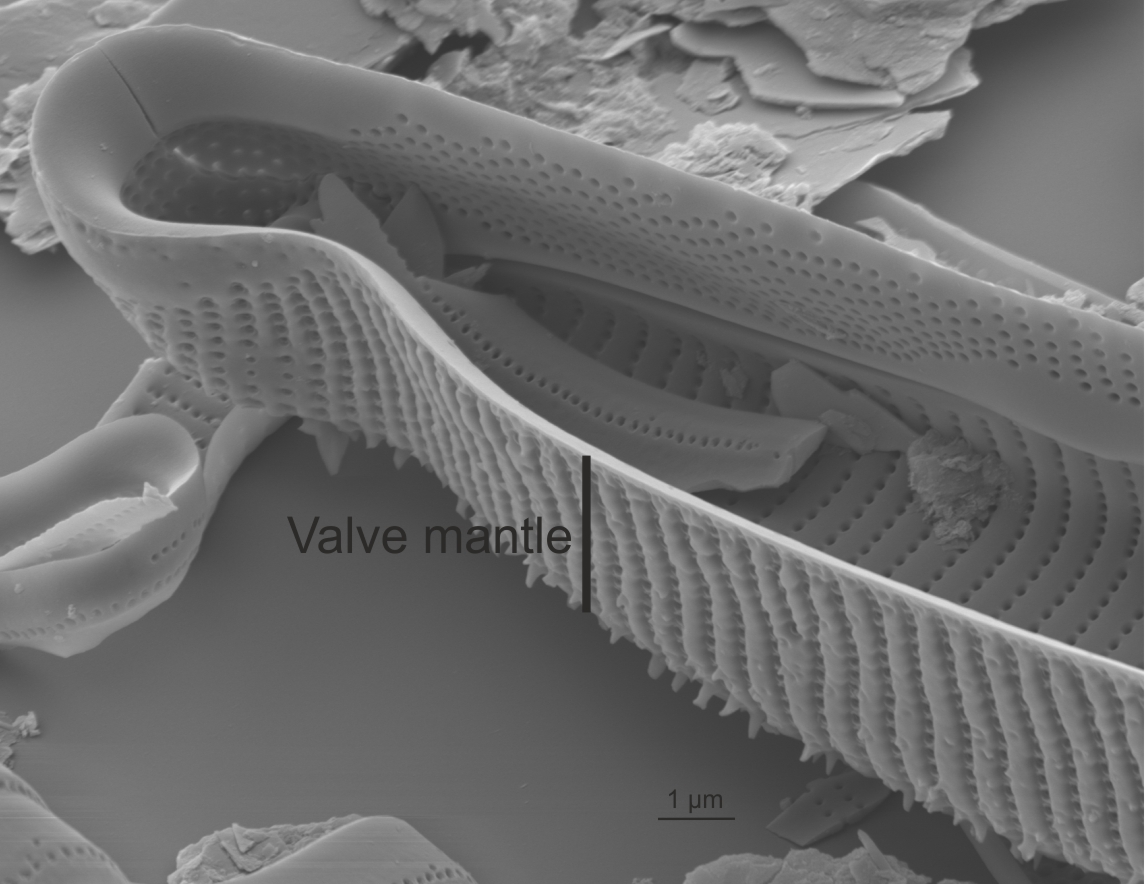 Mantle in Eunotia (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Valve: symmetry |
Shape of valve in relation to apical and transapical axes. The apical axis is defined as the long axis of a pennate diatom (and may be curved), the transapical axis is at right angles to this.
Anonymous. 1975. Proposals for standardization of diatom terminology and diagnoses. 53. Nova Hedwigia, Beihefte. 323-354 pp
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Cox E.J. 2012. Ontogeny, homology, and terminology - wall morphogenesis as an aid to character recognition and character state definition for pennate diatom systematics. Journal of Phycology. 48: 1-31.
Notes: Symmetry has been used as a significant discriminating character. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
 Valve symmetry in Navicula (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
 Valve symmetry in Gomphonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
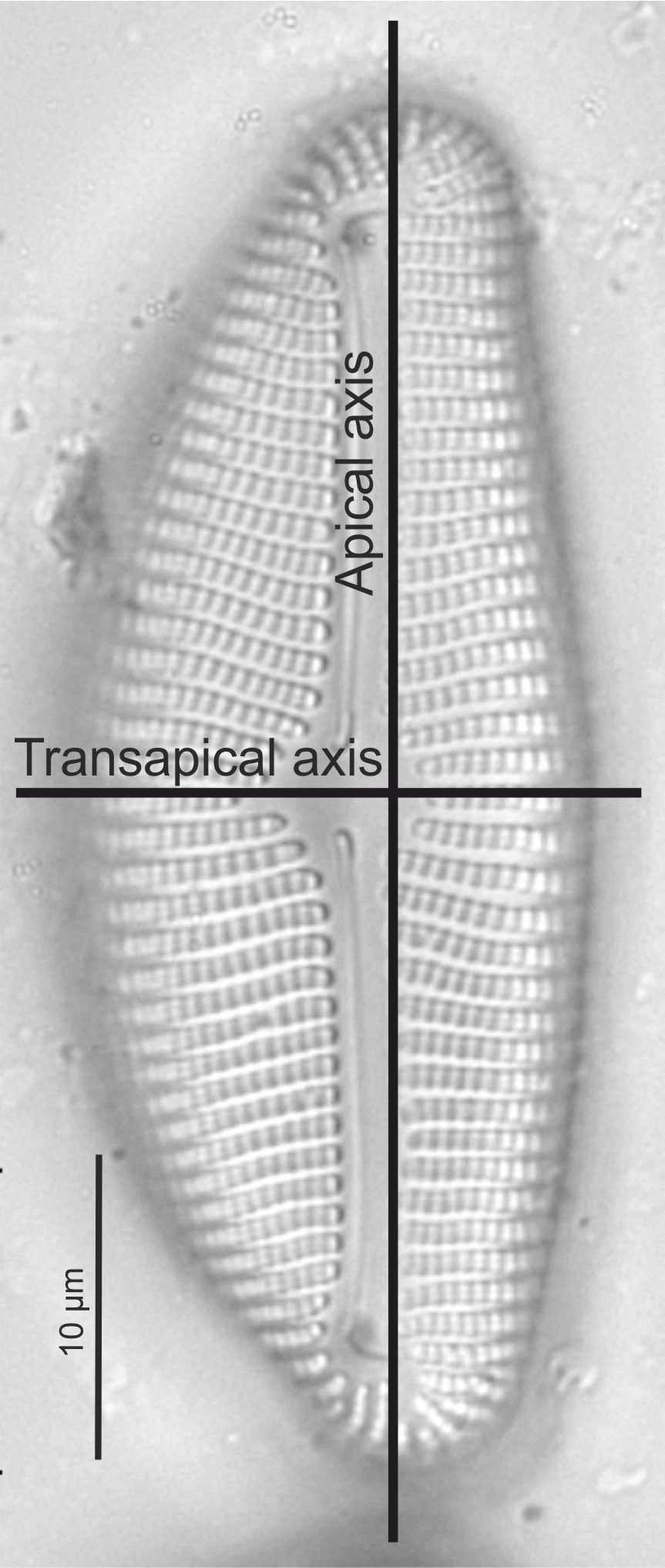 Valve symmetry in Encyonema (LM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|
| Valve: valve face |
The central portion of a valve before it curves down to the girdle region.
Round F.E., Crawford R.M., Mann D.G. 1990. The Diatoms. Biology & Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 747 pp
Notes: Some species have very clearly defined junctions between valve face and mantle (girdle view); others show no clear distinction between face and mantle. Author(s): Cox E. J.
|
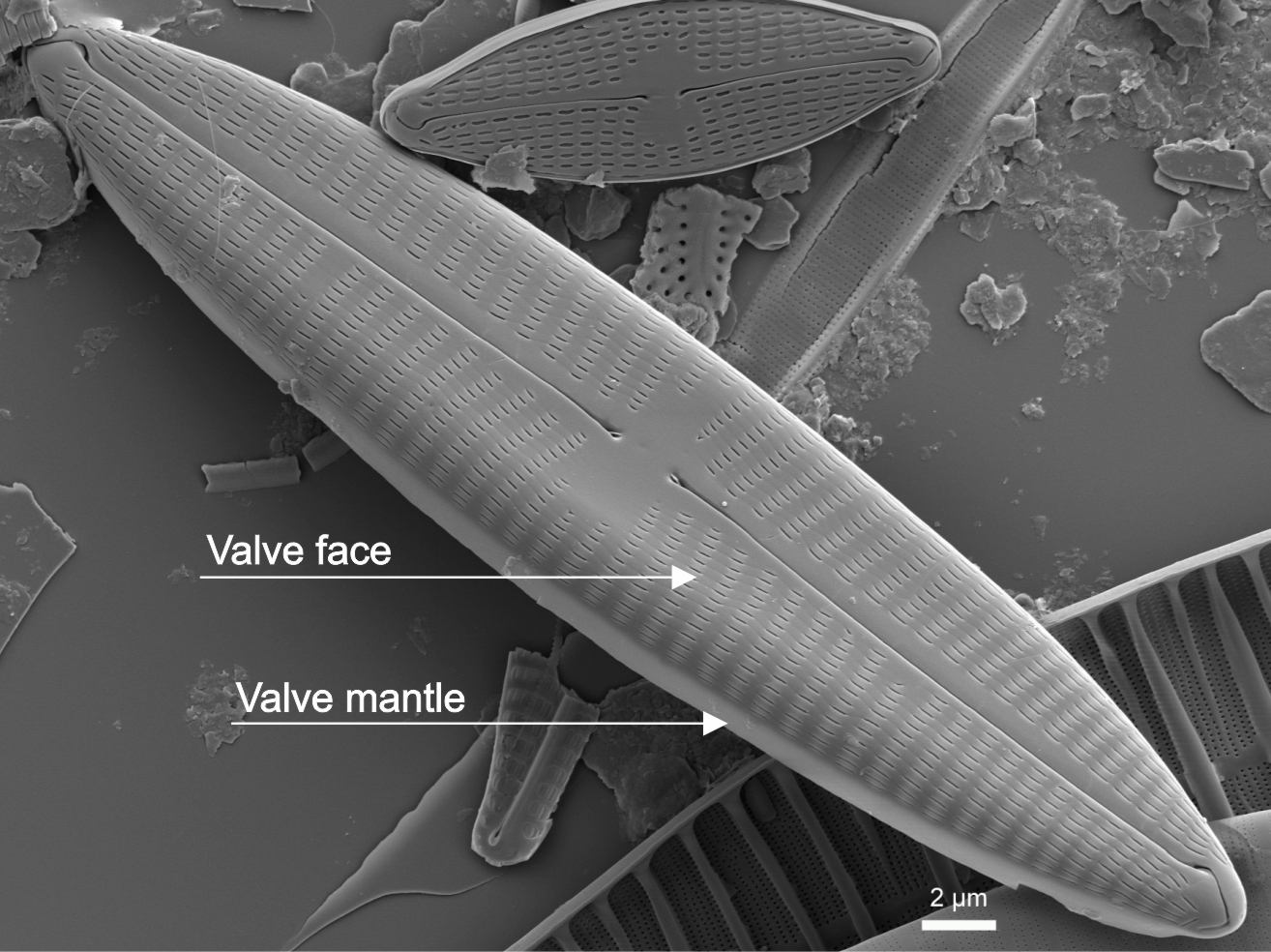 Valve face in Navicula (SEM)
Image: Jüttner I.
|